Hypernasality speech occurs when there is an abnormal increased nasal airflow during speech. Hypernasality may affect children and adult with cleft lip and/or palate with uvula or soft palate dysfunction when producing speech. Speech quality is affected when it deviated from typical range of speech quality.
Let’s Learn How Speech is Process
The palate structure can be divided into hard palate and soft palate. The soft palate connect to the uvula, a small muscle tissue at the back of the roof of the mouth. The uvula is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone. Uvula functions to close the gap between nasal and oral cavity during speech production by elevating and retracted when producing nasal sounds such as /m/ and /n/.
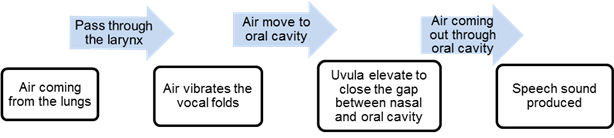
Almost all of the speech sounds are produced by air coming out through the oral cavity, but some speech sounds are produced by air coming out through the nasal cavity (nasal sounds). The nasal sounds are /m/, /n/, /?/ and / ?/. At rest, the uvula are lowered and not elevated when producing nasal sounds.
A Cause of hypernasality
-
Hard palate and soft palate cleft
Children born with cleft palate are at high risk of developing hypernasality speech quality. The cleft palate causes the excessive air to come out through the nasal cavity during speech. Velopharyngeal incompetence or insufficiency is the result of a shorter uvula structure and incomplete closure comparing to typically developing children
- Neurological Deficits
The uvula movement is innervated by a nerve; children with neurological deficits such as cerebral palsy might have uvula incompetence. The uvula does not elevate when speech sounds are produced.
- Hearing Problem
Saringan pendengaran perlu dilakukan pada kanak-kanak yang mempunyai masalah sengau. Kanak-kanak yang mempunyai masalah pendengaran juga berisiko tinggi untuk A hearing screening should be done when a child has hypernasality. Children with hearing problems may at risk of hypernasality due to inability to hear speech sounds clearly than typical developing individuals.
The Identification of Hypernasality
The Speech-Language Therapist is the professional who diagnose and treat individuals with hypernasality. They mostly do so by collecting speech samples from children to detect if any speech sound errors occur during speaking.
When diagnosing hypernasality, a small mirror is put under the nostril and child is asked to produce an oral sounds. If mist occur on the mirror when producing oral sounds, the child may need a further assessment for hypernasality.
An endoscopic evaluation by the Ear, Nose and Throat doctor is among the further objective assessment suitable for identifying the hypernasality. A flexible camera is inserted through the nasal cavity to the uvula in order to observe uvula mobility and sufficiency when speech sounds are produced.
Treatment
The following treatment is suitable for hypernasality in children.
- Surgery
A surgery involving a closure of the cleft of hard palate or cleft of the soft palate may help in reducing the gap between the uvula and back of the throat in order to alleviate the hypernasality voice quality. - Prosthesis
A speech prosthesis is prepared by the orthodontist to help children with hypernasality due to cleft palate. The speech prosthesis will be placed on the palate and will help to reduce hypernasality quality. - Speech Therapy
Several exercises can be taught in the speech therapy in order to strengthen up the muscles of the soft palate. The oral motor exercise is provided to increase air flow throughout the oral cavity and to increase speech intelligibility.
The techniques below might be helpful in reducing the hypernasality.
-
Auditory feedback : The children will be trained to be aware of the difference between normal and nasal speech. This technique is taught by training them to listen to speech production via a listening tube.
Using their listening, have the child put one end of the tube in the entrance of a nostril and the other end near to his ear. When nasality occurs, it is very loud through the tube. Then, ask the child to try to reduce or eliminate sound coming through the tube as he produces oral sounds and words.
-
Visual feedback
Using the See Scape, the child will be trained to reduce hypernasality by controlling the air by controlling the stopper in the See Scape from rising up. The child will be asked to produce pressure consonant repetitively without allowing the stopper from rising up by adjusting the speech production.
-
Cul De Sac technique
The child will be asked to pinch his/her nostrils during the production of pressure sounds to eliminate the nasal air emission throughout the nose. A nose clip can be used during therapy and practice. The child will be taught to note the increase in oral airflow and pressure. Then, the child try to produce the sounds in the same way with the nostrils unoccluded.
-
Exercise
Blowing candle, tissue or a ping pong ball and blowing using straw might be helpful to increase air flow through the mouth.
-
References
-
Kummer, Ann W., 2002, Speech Therapy for Cleft Palate or Velopharyngeal Dysfunction (VPD). Retrieved September 1, 2012 fromhttp://arslpedconsultant.com/documents/velopharyngeal%20dysfunction%201.pdf.
-
Serres, D. L. Hypernasality – Velopharyngeal Insufficiency(n.d); Retrieved September 5, 2012 from http://www.entcolumbia.org/hypernas.html.
-
Kummer, Ann W., 2005, Speech Therapy for Characteristics Of Velopharyngeal Dysfunction (VPD);Retrieved September 1, 2012 from http://www.superduperinc.com/handouts/pdf/96_velopharyngeal.pdf
-
Hypernasality Speech (n.d); Retrieved August 28, 2012 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypernasal_speech.
-
Hypernasality Program(n.d);Retrieved August 28, 2012 from http://childrensnyp.org/mschony/otolaryngology-hypernasality.html.
| Last Reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writer / Translator | : | Nurul Fatehah bt. Ismail |
| Accreditor / Reviwet | : | Nadwah bt. Onwi |







