What Is OPG?
- OPG is an x-ray to visualise the teeth and gums.
- It is used by doctors to identify dental problems and to help decide on treatment.
Reasons For OPG
- To identify the cause of tooth-ache or swelling of the gums.
- To identify teeth which are not in alignment.
- To plan treatment for a cavity in the tooth or surgery of the root of the tooth.
- To plan for orthodontic treatment.[1]
How Can I Get This Examination Done And Where?
- The doctor you are seeing will decide if you need the examination.
- If it is necessary, the doctor will make a request for examination using Request Form For Radiological Examination.
- This examination is available in selected Ministry of Health hospitals.
Before OPG
- The radiographer will explain the process and the position that will be required.
- Please inform the radiographer if you are pregnant or may be pregnant.
- You will need to remove metallic objects such as hair-clips, earrings and necklace to avoid image artifacts.
During OPG
- Your name will be called and you will be showed into the examination room.
- You will be given a lead gown to wear as a protection against scatter radiation.
- You will be asked to stand near the OPG machine.
- The radiographer will position you.
- The radiographer will then make an X-ray exposure to acquire the image.
- During the X-ray exposure, the X-ray tube will rotate around your head. Please do not move while the machine is moving. The movement will not cause you any harm.
After OPG
- The radiographer will move you out of the OPG machine.
- Take out the lead gown.
- You may leave the department after the examination.
 |
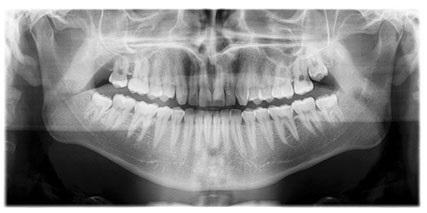 |
| Positioning for OPG | All teeth and gums shown |
Picture 1: The required positioning and OPG image
Source: www.gendex.com/US/Products/Panoramic-X-ray-Systems/Gendex-GXDP-300.aspx
New Technique
- New technique for X-ray of the teeth is known as Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT).
- Images produce by CBCT can be manipulated and post-processed to visualise the teeth and gums from different direction.
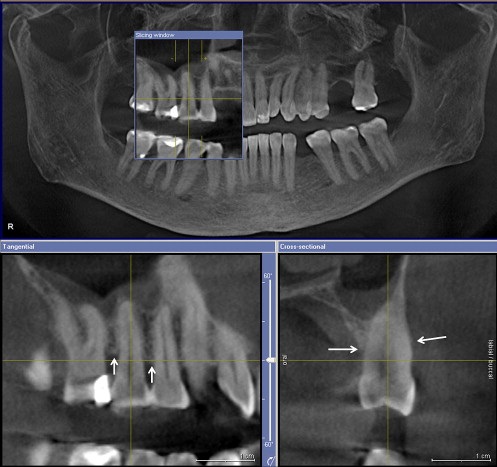 |
Picture 2: Image from CBCT and image of a tooth which has been rotated.
Source: www.reedyforddental.com/cone-beam-referrals.html
Reference
-
Gendex GXDP-300™, Digital Panoramic X-ray System, http://www.gendex.com/US/Products/Panoramic-X-ray-Systems/Gendex-GXDP-300.aspx
-
Reedyforddental centre, cone beam scanning, http://www.reedyforddental.com/cone-beam-referrals.html
-
Panaromic Radiograph, 2014, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Panoramic_radiograph
| Last Reviewed | : | 5 January 2017 |
| Translator | : | Daud bin Ismail |
| Accreditor | : | Irene Tong Lee Kew |







