What is Bleeding Tendency?
It’s a condition whereby someone suffers from prolonged bleeding when having a cut or injury. In terms of dental procedures, tooth extraction and scaling can bring about bleeding episodes in children with bleeding tendencies. Therefore avoidance of these conditions which are actually preventable must be of prime importance in the oral health care of these children.
In a normal child control of bleeding involves
- contraction of blood vessels
- clumping together of platelets (a constituent of blood)
- blood coagulation.
Any defect in these will lead to a bleeding problem.
Thus patients with these conditions will tend to have a bleeding tendency:
- Platelet abnormalities: Either a reduction in the number of platelets or a defect in platelet function will cause a person to have a tendency to bleed. This may be related to other diseases e.g. Aplastic anaemia and Leukemia.
- Blood coagulation problems like Hemophilia, Christmas Disease, Von Willibrands Disease, liver diseases or deficiency in any of the clotting factors.
- Medications that affect the platelets or coagulating factors e.g. Aspirin, Warfarin and Heparin.
- Blood vessel anomalies e.g. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, scurvy or vascular malformation
A child with leukemia have a lower platelet count causing them to be prone to bleeding.
Bleeding may occur spontaneously especially if the patient has gingivitis. This is worsened when an invasive treatment is done.
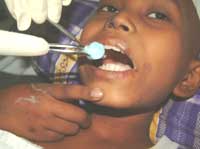
The picture shows a child with leukemia having his teeth cleaned with Chlorhexedine mouthwash.
Why is oral health so important in these children?
A healthy mouth is vital in children with bleeding tendencies. Poor oral health and hygiene will cause the gums to be inflamed. Gums that are inflamed are unhealthy and appear spongy,red, and bleed easily. When inflamed gums bleed, the bleeding is difficult to control, and this situation is worsened in a child with bleeding problems.
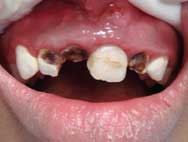
Poor oral hygiene leads to gingivitis and caries.
Poor oral health in a child will lead to grossly carious teeth and unhealthy gums. Doing large restorations, scaling and extractions may cause a child with bleeding tendencies to bleed profusely if the necessary precautions to prevent complications are not taken. This risk is avoided with good oral healthcare.
How can we provide good oral healthcare for these children
- Brushing children’s teeth
- Children’s teeth should be brushed 2-3 times a day.
- The night brushing before bed is most important.This is to ensure that a child sleeps with a clean mouth everyday.
- An adult should help with the brushing in children less than 7 years of age. This is very important because young children do not have the skills to clean effectively.

Young children need to have their teeth brushed by an adult, especially before bedtime
- Children over the age of 7 can brush their own teeth, however adults need to monitor the effectiveness of their brushing.
Which toothpaste should I use?
-
- Young children by the age of 2 should use a fluoridated child’s toothpaste, these will have about 500-600ppm of fluoride. However only a smear or pea sized amount should be used.
- Once a child is able to rinse effectively, they can start to use an adult toothpaste. Toothpastes for adults have a higher fluoride content and this will give greater protection for the child’s teeth.
- In a child of normal intelligence and dexterity, this should be true by the time the child is aged 7 years or older
How do I choose an effective brush to use for my child?
Choose a soft brush that is suitable for your child’s size and age. Replace with a new brush every 3-4 month or when the bristles are splayed.
Will there be any risk of bleeding when I brush my child’s teeth?
Children with low platelet levels (<20×109 /l) may have gingival bleeding from toothbrush trauma or even spontaneously. For these children brushing may be contraindicated and swabbing with Chlorhexedine mouthwash may have to suffice until the child’s condition stabilizes. Otherwise there is no contra-indication to brushing in children with bleeding tendencies. In fact brushing make their gums healthier and less likely to bleed.
- Diet Control
How do I control their diet to maintain good oral health?All sugary foods and drinks may cause decay. This includes sweet cakes/breads, biscuits, cordials and carbonated drinks.
It is very difficult to totally avoid sugar in your child’s diet.
The important thing is to identify the sugary foods especially the sticky ones like toffies, limit its intake, and to know how to take it safely.The frequency of sugary food/drinks intake
- The frequency of sugary food/drinks intake plays a big role in causing caries. Acids that cause tooth decay, form in your mouth every time you eat a sugary snack. These acids are formed by bacteria using the sugars present in your mouth. Once formed, it takes at least 20 minutes for these acids to be neutralized So, the more times you eat sugary snacks during the day, the more often you provide fuel to the bacteria to cause tooth decay 3.
- Try to limit sugary food/drinks to after main meals i.e. after breakfast / lunch / dinner 5. (After which the child’s teeth needs to be brushed)*
- If your child frequently asks for drinks, only give plain water or plain milk, in between meals 5. Limit sweet drinks to meal times.*
- Give your child healthy snacks instead of sweet ones e.g. keropok, kacang rebus, fruits and bread. Avoid giving sugary snacks.

All sugar containing food and drinks may cause decay, not only sweets and chocolates.During bed time
During sleep our saliva stays stagnant in the mouth with any remnant food debris. This is the time whereby any remnant sugar sources in the mouth can cause the most destruction of tooth substance. To prevent decay brushing before bed time is very important.

After brushing before bedtime, there shouldn’t be anymore eating/drinking except for drinking plain water.
Is your child still bottle feeding?
Children should be weaned from the bottle from the age of 12 to 14 months 1,2. Avoid giving your child flavored milk/drinks.
Prolonged bottle feeding will cause a child’s dentition to develop severe early childhood caries.
Children over the age of one should be taught to use a cup for drinking milk.
- Visiting the dentist.
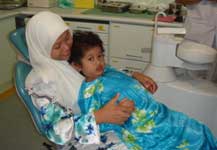
Children with bleeding tendencies need close monitoring and care of their teeth and gums. A periodic visit is recommended so that early preventive treatment can be done. This will make it easier for the child to accept treatment and get used to visiting the dentist.It must be remembered though that the dentist should always be informed of the child’s bleeding tendency or any other medical condition.
References:
- Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Severe Early Childhood Caries. Ministry of Health Malaysia, July 2005
- Council on Clinical Affairs. Policy on Early Childhood Caries: Classifications,Consequences, and Preventive Strategies.Oral Health Policies. Reference Manual. 2004-2005
- National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. Children’s Oral Health. www.nidcr.nih.gov
- Porter, S.R., & Scully, C. (Eds) (1995) Oral Health Care for those with HIV infection and other special needs. London:Lonsdale Press Limited.
- Rugg-Gunn, A.J. (1997) Dental Caries. In Welbury R.R (Ed), Paediatric Dentistry (pp95-113) Oxford University Press
- Shaw, L. (1997) Medically Compromised Children. In Welbury R.R (Ed), Paediatric Dentistry (pp353-371) Oxford University Press.
| Last Reviewed | : | 25 April 2014 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Sa’adah bt. Atan |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Laila bt. Abd. Jalil |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Hjh. Noraini @ Nun Nahar bt. Yunus |







