The mouth is the home to over 700 different types of microorganisms. Most are harmless and some are even probably good. However, maintaining good oral health is important to reap the benefits of the ”good bacteria” and keep the ”bad bacteria” in check.
Oral infections can be divided into 3 major causes: bacterial, viral or fungal.
Bacterial infection
- The most common bacterial infections in the mouth are dental caries (dental decay) and periodontal diseases (gum diseases).
- Generally, infections caused by bacteria can lead to collection of pus at site of infection.
- Thus if untreated, infections from the teeth and gums can spread to adjacent soft tissue or bone to form pus-filled pocket of infection (dental abscess) or widespread inflammation (cellulitis).
- Swelling, pain, redness of the overlying skin and fever are the common signs and symptoms.
- Treatment includes draining the pus, antibiotic therapy (if there is sign of fever or spreading infection) and most importantly the removal of the cause of infection such as extraction of the offending badly decayed tooth.
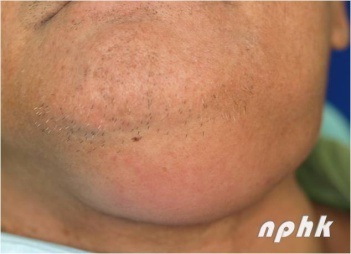
Fig. 1 Dental Abscess
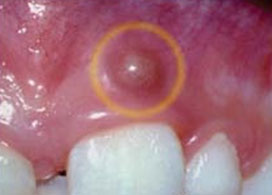
Fig 2. Dental Abcess on the gum
- Severe infection from lower teeth involving the floor of the mouth may compromise the airway leading to breathing problems, whereas those from the upper teeth may potentially spread to the brain.
Viral Infection
- Most frequently seen viral infection in the mouth is due to herpes simplex virus known as primary herpetic gingivostomatitis which occurs largely during childhood or adolescence.
- Main presenting complaint – multiple mouth ulcers which are painful and can occur all over the mouth.
- Ulcers may be preceded by small vesicles or blisters. Gums are also often red and swollen.
- Fever and general feeling of unwell are also common.
- Infection is usually self-limiting and resolves within 14 days.
- Treatment is generally supportive symptomatic therapy to ease the pain and fever.
- Recurrent infection may occur anytime throughout and commonly present on the lip as herpes labialis or cold sores
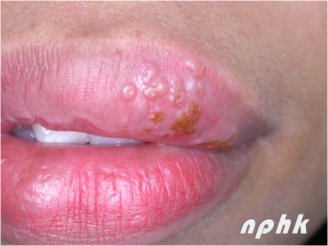
Fig. 3 Cold sores or Herpes labialis
- Cold sores appear as multiple fluid filled vesicles which later breakdown on form crusting.
- In many cases, no active treatment indication. However, early application of topical anti-viral medication can reduce the duration of cold sores.
- As the virus spreads easily through saliva, limited contact with lips and mouth during active disease is advisable to reduce risk of spread of infection to other sites.
Fungal Infection
- Generally, fungal infections may occur in the mouth when the host immune response is compromised.
- Hence, they are known as opportunistic infection.
- Most commonly encountered fungal infection in the mouth is ”thrush”. Clinically, the infection present as creamy whitish spots or patches which can be rubbed off to leave a reddish, raw area. Occur anywhere in the mouth especially the palate and cheek.
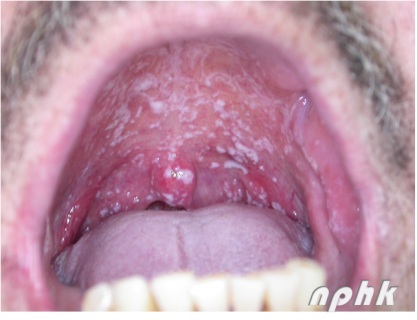
Fig. 4 Oral thrush
- This condition may affect the debilitated elderly, patients undergoing treatment for cancer or on long-term steroid therapy, those infected with HIV and others
- Severe dry mouth can also be a predisposing factor.
- Can also present primarily as red areas especially on tongue and palate.
- May also present with associated burning sensation or pain.
- Treatment involved use of either topical or systemic antifungal medication. However, the underlying condition also needs to investigated and addressed appropriately.
| Last Reviewed | : | 20 April 2012 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Nurshaline Pauline Hj. Kipli |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Marzuki b. Zainal Abidin |







