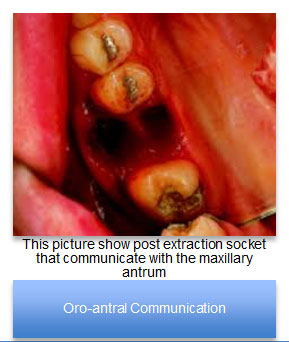
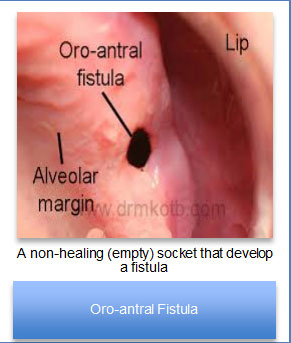
What is oro-antral communication (OAC)?
What causing OAC?
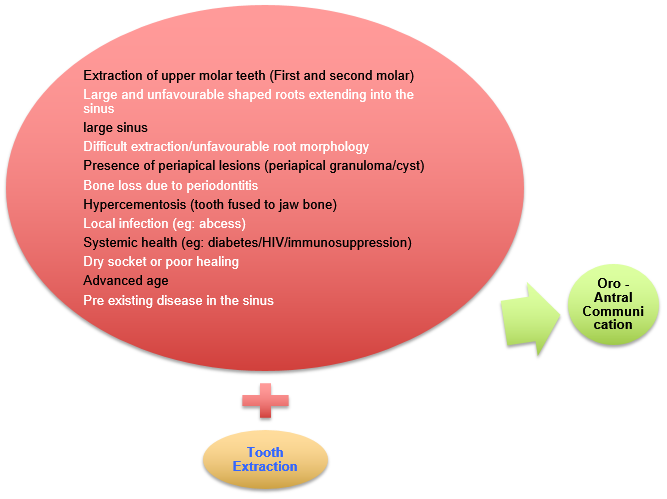
What factor put you at risk developing OAC after tooth extraction?
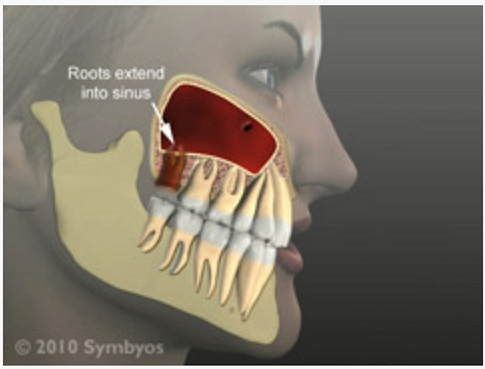
*Large and unfavourable shaped roots extending into the sinus
What are the signs and symptoms?
Following the creation of an oro-antral communication, the patient may experience various signs and symptoms including :
Symptoms
- Escape of fluids from mouth into nose on eating/drinking
- Air or fluid into mouth on blowing the nose
- Pain initially – over time it would only be painful if there was an added infection
- A blocked nose and discharge on the one side (feeling of fullness)
Signs
- Fracture of the antrum floor
- Attachment of sinus lining and associated fractured bone and roots upon extraction
- A non-healing/empty socket (Loss of the socket blood clot in the days immediately following extraction)
- Persistent pain localized to tooth socket
- Pain and tenderness of the area under the eye/upper cheek on one side
- Dark opening into the sinus visualized with appropriate lighting
Pain severity: Usually not painful unless secondary sinusitis develops.
If you have an OAC, what will happen?
Two things can happen:
- It can heal spontaneously– As usually happens with the appropriate care
- An oro-antral fistula forms– here the gum in your mouth and the lining of your nose cavity grow together to form a non-healing tunnel between the two. It requires further surgery to close.
The dentist may suspect a communication, or one may have been confirmed. Either way, the advice is similar- you should follow their instructions, which are aimed at preventing a rise in air pressure in the sinus. If this happens, for example sneezing or blowing your nose will force air down into the mouth, through the hole and it may worsen or prevent the communication from healing.

Reminder: Follow all extraction aftercare advice!
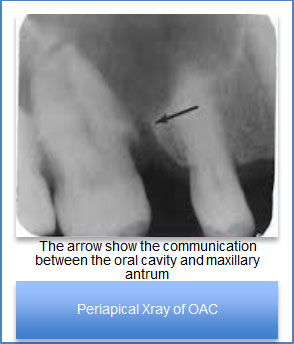
How to investigate?
|
Objective of the investigation |
Methods |
|
To demonstrate communication between antrum and mouth |
|
|
To detect retained root fragments or sequestra in socket or into antrum. To exclude the possibility of other lesions such as malignant neoplasms |
Radiographs: Periapical (PA view), Orthophantomogram (OPG)/Occipto-mental view (OMV)/CT scan |
|
To eliminate dental causes for any pain |
Vitality test, mobility of the adjacent teeth |
|
To exclude malignancy or identify other causes for impaired socket healing |
Biopsy (if presence of solid tissue in the socket) |
*Radiological observations might show a sinus floor discontinuity, sinus opacity or focal alveolar atrophy.
|
|
How to treat the OAC?
Decision on how to treat an OAC is base on the size of communication, time of diagnosis and presence of an infection
Estimate the fistula diameter
-
1-2 mm: No treatment required, as it will usually naturally heal.
-
2-4 mm: Carefully follow the patient after 1-2 weeks and advise to avoid straining the area (no holding back sneezes, no smoking, no use of straws, no pressure on the sinus).
-
6 mm or larger: the primary purpose is closure of the defect and prevention of sinusitis. Immediate management will includes:
- Suturing/periodontal pack
- Rinses with physiologic solution
- Rinses with antibiotic solvent
- Antibiotic prophylactic
- Consequently, the treatment usually involves surgical intervention. Various techniques have been reported in the literature including local flaps (e.g., palatal rotational advancement and buccal advancement flaps), distant flaps (e.g.tongue flaps) or grafts (e.g., bone graft)
Possible Complications of OAC
- Chronic sinusitis
- Facial cellulitis
- Osteomyelitis with maxillary bone loss (less common)
References
- Borgonovo, A.E., Berardinelli, F.V., Favale, M. et al (2012) Surgical Options In Oroantral Fistula Treatment. Open Dent J. 2012; 6: 94–98.
- Canadian Dental Association (2013). How Do I Manage Oroantral Communication? Key Points. URL http://www.oasisdiscussions.ca/2013/03/19/oc-2/
- Cankaya, A.B., Erdem, M.A., Cakarer, S., Isler, S.C, Demircan, S., et al. (2012) Reliability of Two Surgical Methods for Oroantral Communication Closure; A Clinical Study of 20 Patients. Otolaryngology 2:113. doi:10.4172/2161-119X.1000113
- Dym, H., Wolf, J.C. (2012) Oroantral Communication. Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin N Am 24; 239-247
- Logan, R.M., Coates, E.A (2003) Non-surgical management of an oro-antral fistula in a patient with HIV infection. Australian Dental Journal 2003;48:(4):255-258
- Workman, J. (2012). Oro Antral Communication. URL http://jamiethedentist.com/oro-antral-communication/what-is-an-oroantral-communication
| Last Reviewed | : | 6 October 2015 |
| Writer / Translator | : | Dr. Rohaizar bt. Ismail |
| Accreditor | : | Dato’ Dr. Rusdi bin Abd Rahman |