What Does Paranasal Sinuses X-ray (PNS) Mean?
X-ray of the sinuses or paranasal sinus radiography is X-ray examination which can be performed with minimal discomfort.
What Are Sinuses?
Sinuses are air – filled spaces (cavities) which are lined with mucous membranes within the skull bones (1).
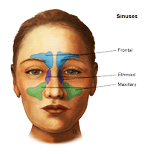 Figure 1: The various sinuses in our skull (2)
Figure 1: The various sinuses in our skull (2)
Who Performs The PNS X-ray?
The PNS X-ray is performed by a radiographer and the image is interpreted by a radiologist.
When The PNS X-ray Is Requested?
- The PNS X-ray is requested (2) when the patient experiences blocked sinuses due to too much of mucous build up, bacteria and germ which leads to infection and inflammation of the sinuses and is referred to as sinusitis (infection of the sinuses).
- Other sinuses related problems such as deviated septum.
- Symptoms of other infection in the head area.
- To detect injury/ other problem within the sinus.
- To determine the size and location of tumor or mass.
- To evaluate the patient after sinus surgery.
What Projections/ Views Are Performed?
Routinely three projections/ views are performed which are namely the lateral view, occipital frontal (OF) view and finally the occipital mental (OM) view.
What Are The Patient Preparation For The PNS X-ray?
Typically there is no special preparation required:
- Female patients who are in the child bearing age capacity, the LMP is asked to ensure the woman is not pregnant (5 & 6).
- The radiographer should be notified if the patient has a prosthetic (artificial) eye as it can cast a shadow causing confusion to the sinus area (2).
- Patient need to remove object within the skull/ head e.g. hair clips, earrings.
What Takes Place During The Examination (3)?
- Following this, the patient is advised to remove jewelry or any metal objects from the area of the head.
- Lead apron may be provided for radiation protection.
- Often the patient is positioned in the sitting (upright) position facing the detector. The radiographer positions the patient’s head in three (3) position whereby either head extended for the OM view; chin tucked for the OF view and the lateral view with the head turned to the side. For all views it is necessary for patient to hold still as it will cause blurring of image and requiring a repeat examination.
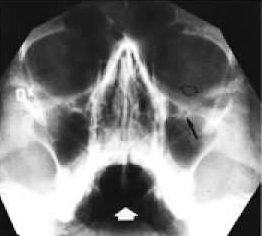
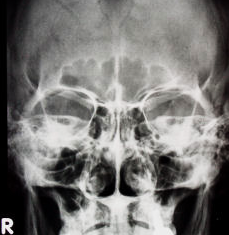
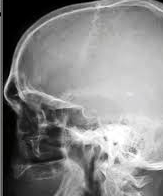
Radiographic Appearance Of The PNS X-ray
Figure 2: Occipito meatal (OM) view | Figure 3: Occipito frontal (OF) view | Figure 4: Lateral view
What Happens After The PNS X-ray Procedure?
- There is no special instruction or preparation required.
- The patient is allowed to leave the department once the examination is over.
- The result of the examination will be sent to the requesting doctor.
References
- Checking The Pregnancy Status of Females of Childbearing Age. University Hospitals of Leicester, National Health Services, UK. (http://www.library.leicestershospitals.nhs.uk/pubscheme/Documents /Services%20we%20offer/Patient%20informat ion/Imaging/ADULTS/Radiology%20 %20Checking% 20Pregnancy%20Status%20Edition%204-7125284%20-%20UHL%20Patient%20Information%20-% 20Imaging.pdf)
- Imej pada PNS x-ray. (https://www.google.co.uk/search?q=images+on+PNS+x-ray&tbm=isch&tbo=u&source=univ&sa=X&ei=KsrcU8WbFtGzuATDx4DAAQ&ved=0CCgQsAQ&biw=1708&bih=841&dpr=0.8#facrc=_&imgdii=d4MPoWQSL5EyoM%3A%3B0r2lB8ZxFGmkoM%3Bd4MPoWQSL5EyoM%3A&imgrc=d4MPoWQSL5EyoM%253A%3BP7snR_i5YC2BaM%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.drtbalu.com%252Fimages%252Flat%252520.jpg%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.drtbalu.com%252Fxrays_rhino.html%3B300%3B365)
- Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia. Guidelines for Medical Diagnostic Procedures Using X-Ray in Women of Childbearing potential. (http://radia.moh.gov.my/project/radiaweb/docs/10_dan_28% 20Day%20Rules.pdf)
- Radiology now. The “10-Day Rule”DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1259/0007-1285-46-551-933. Terbit atas talian 28 Januari 2014. (http://www.birpublications.org/doi/abs/10.1259/0007-1285-46-551-933)
- Sinus Pain attack. (http://www.medicinenet.com/sinusitis_pictures_slideshow/article.htm)
- Sinus x-ray. (http://www.healthline.com/health/sinus-x-ray#Overview1)
- Sinus X-ray. (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003803.htm)
- Sinus X-ray. (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003803.htm)
- The 28 Day Rule. (http://www3.ha.org.hk/qmh/department/Clinical%20Department/Radiology/ xray.htm)
- What does a Sinus x-ray diagnose (http://www.healthline.com/health/sinus-x-ray)
| Last Reviewed | : | 2 June 2016 |
| Writer | : | Pushpa Thevi Rajendran |
| Accreditor | : | Daud bin Ismail |