Introduction
Hemophilia is the blood clotting disorder caused by deficiency of clotting factor in the blood. Some study concluded that Hemophilia is one of hereditary genetic disorders. It can occur to anyone. Hemophilia is more likely to occur in males than females.
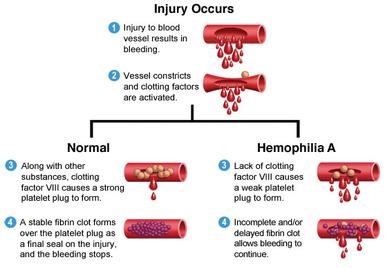
Clotting factor is used to stop the bleeding when the blood vessel is broken. The clotting factor will stimulate the blood vessel to constrict when the bleeding happens. The cell will aggregate on each other until they stop the bleeding (PICTURE 1).
The coagulation activity will be impaired when abnormal clotting process occurs (PICTURE 1.).
How Hemophilia Occur?
The coagulation factors needed for a normal clotting process. People with Hemophilia have lower clotting factor level of blood plasma. PICTURE 1 shows the comparison of the blood clotting process among normal and the person with Hemophilia.
Normal person have normal clotting factor level of blood plasma that needed for a normal clotting process.
 |
| Example: Bleeding in normal person (PICTURE 1) |
| Source: genetic-disorder-wiki.wikispaces.com |
| Normal | Hemophilia |
|
a) Injured blood vessel will cause bleeding. b) Constriction of the blood vessel occurs. c) Injured vessel blocked by trombosit. d) Coagulation factors will stimulate the fibrin formation which is necessary to maintain the blood clot.
|
a) Thus when a blood vessel is injured and forms the temporary scab b) Constriction of the blood vessel occurs. c) Injured vessel blocked by trombosit. d) Missing coagulation factors prevent fibrin formation, which is necessary to maintain the blood clot. A hemophiliac does not bleed more intensely than a person without it, but can bleed for a much longer time. |
Factors
There are two types of Hemophilia:
- Hemophilia A
Hemophilia A (clotting factor VIII deficiency) is the most common forms of the disorder. From the statistic by International Hemophilia Congress of United State, 85% of Hemophilia are from this group.
2. Hemophilia B
Hemophilia B occurs with factor IX deficiency.
Aim of Physiotherapy Management
- To control the pain and inflammation
- To maintain available affected and unaffected joint range
- To increase the affected joint range
- To strengthen the affected muscle
- To assist in maximum daily function
- To prevent deformity
Signs & Symptoms
Hemophilia can cause spontaneous and prolong bleeding at any muscle, joint and internal organ. The complication is not only pain but can cause handicap and death.
Complications
- Limitation in daily activity due to pain
- Spontaneous bleeding over the joint
- Inflammation over the joint cartilage that can cause deformity if not treated
- Muscle atrophy (wasting) can cause weakness if not used
- Muscle shortening can cause contracture if not stretched
- Brain bleeding can cause permanently paralyze and mental retardation if not treated early
- Bleeding inside the important muscles of pelvic
Prevention
- Avoid participation in high loading activity eg jumping and contact sports eg soccer, rugby, boxing, jumping, basketball, skating, skiing etc
- Must always be cautious and carefull to prevent any injury in sport
- Low impact activity eg cycling and walking and non contact sports eg bowling, tennis, jogging, snooker, golf, ping pong, darts are advisable
Physiotherapy treatment
- Acute Phase (bleeding)
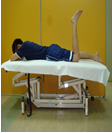
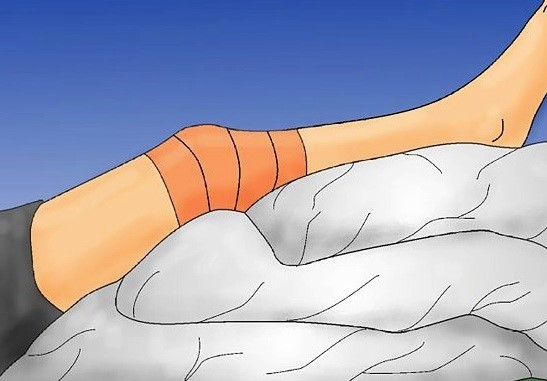
| i | Rest | : | Support and rest the affected limb on the pillow (PICTURE 2) |
| ii | Ice | : | Wrap the affected joint with the ice & let it for 15-20 minutes. Do not apply any heat ointment before the treatment to prevent any complication |
| iii | Support | : | Support the affected joint with the splint for enhance the healing process (PICTURE 3) |
| iv | Exercise | : | Keep moving the unaffected joint to maintain optimum joint range and muscle length |
 |
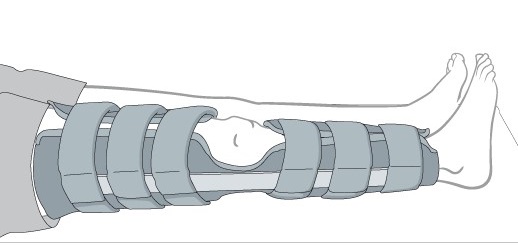 |
| Example: Support the limb (PICTURE 2) | Example: Splinting (PICTURE 3) |
| Source: piratstudenterna.se | Source: www2.aofoundation.org |
2. Subacute Phase (reduction of pain & inflammation)
| i | Rest | : | Support and rest the affected limb on the pillow |
| ii | Ice | : | Wrap the affected joint with the ice & let it for 15-20 minutes. Do not apply any heat ointment before the treatment to prevent any complication |
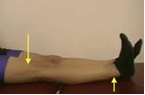
| iii | Support | : | Apply the bandaging on the affected joint to reduce the inflammation (PICTURE 4) |
| iv | Exercise | : |
a) Move actively the affected joint to maintain the available range b) Keep moving the unaffected joint to maintain optimum joint range and muscle length |
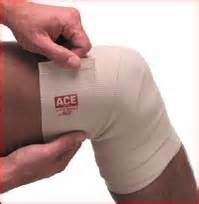 |
| Example: Bandaging (PICTURE 4) |
| Source: painbehindkneetreatment.com |
Chronic Phase
| i | Doctor Management | : | Replacement factor should be prescribed before exercise to prevent any complication (as doctors’ advice) |
| ii | Exercise | : |
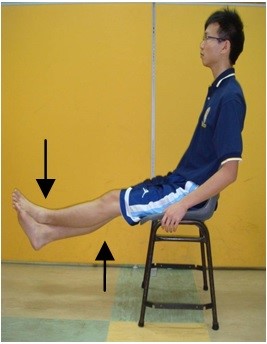
a) Strengthening exercise to strengthen the affected and unaffected limb b) Coordination and balancing exercise to improve body support and trunk control c) Gait training to relearn the normal walking pattern d) Hydrotherapy to improve whole body function and enhance cardiovascular fitness (PICTURE 5) |
 |
| Example: Hydrotherapy (PICTURE 5) |
| Source: www.gosh.nhs.uk |
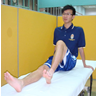
Exercise Prescription:
Example: Exercise Prescription
Source: Jabatan Fisioterapi, Hospital Kuala Lumpur
Reference
- Care protocol OA Knee oleh Jawatankuasa Teknikal Profesion Fisioterapi, KKM
- Guidelines in the management of Hemophilia and von willebrand disease, Draft copy Pusat Darah Negara, 2004
Source Image
- Retrieved Jun 3 2015. genetic-disorder-wiki.wikispaces.com
- Retrieved Jun 3 2015. se
- Retrieved Jun 3 2015. aofoundation.org
- Retrieved Jun 3 2015. com
- Retrieved Jun 3 2015. gosh.nhs.uk
- (2012) Jabatan Fisioterapi Hospital Kuala Lumpur. Retrieved July 4 2013.
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer | : | Pauzillah binti Hj. Dollah |
| Translator | : | Naqiuddin bin Mohd Johar |
| Accreditor | : | Se To Phui Lin |
| Reviewer | : | Halimah bt. Hashim |