Introduction
Patella is your knee cap. When your patella moves out from its natural position it is known as patella dislocation.
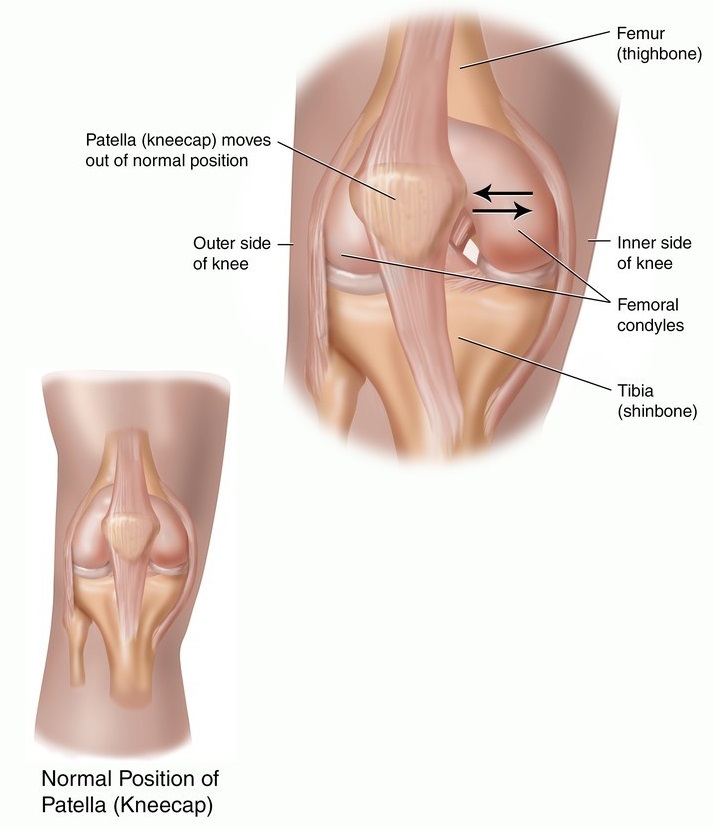 |
|
(Sumber: Hakcipta ©2014 Mc Kesson &/or subsidiaries) |
Causes of patella dislocation :-
- Trauma
Your knee cap can dislocate following a forceful blow or a twisting force to your knee.
- Spontaneous
In some individuals their knee cap can dislocate spontaneously without any particular trauma. This usually happens because of strength imbalance of the thigh muscles.
Signs & symptoms
If you have a dislocated knee cap, you will experience pain at your knee and a swelling will develop around your knee joint. The position of your knee cap will obviously look abnormal.
Consult a doctor immediately so that your knee cap can be repositioned.
A dislocated knee cap if not properly treated can lead to frequent spontaneous dislocation in the future.
Treatment
Your doctor will usually do the following :-
- Examine you and take an x-ray of your knee
- Correct the position of your dislocated knee cap
- Treat any other injuries if present
- Prescribe you with medication to reduce your pain and swelling
- Refer you to a physiotherapist for rehabilitation
Prevention
Recurrent injuries can be prevented through early and effective physiotherapy.
Rehabilitation
These are some of the self-help physiotherapy which you can safely do on your own :-
1. Ice Treatment and Rest
You need to rest your knee from all activities. Placing an ice pack over your knee for 10-15 minutes, 2 or 3 times a day can help to reduce your pain.
To help reduce swelling, bandage your knee and raise it on a pillow. Walk using the aid of crutches so that your knee heals better.
2. Exercise Therapy
Simple exercise therapy can be started once your acute pain subsides; which usually takes a few days. The following simple exercises are recommended ;-
(a) Static Quadriceps Exercise
Tighten the muscles in front of your thigh without allowing any movement in your knee. Hold for 5-10 seconds. Repeat 10 times. Do this every waking hour.
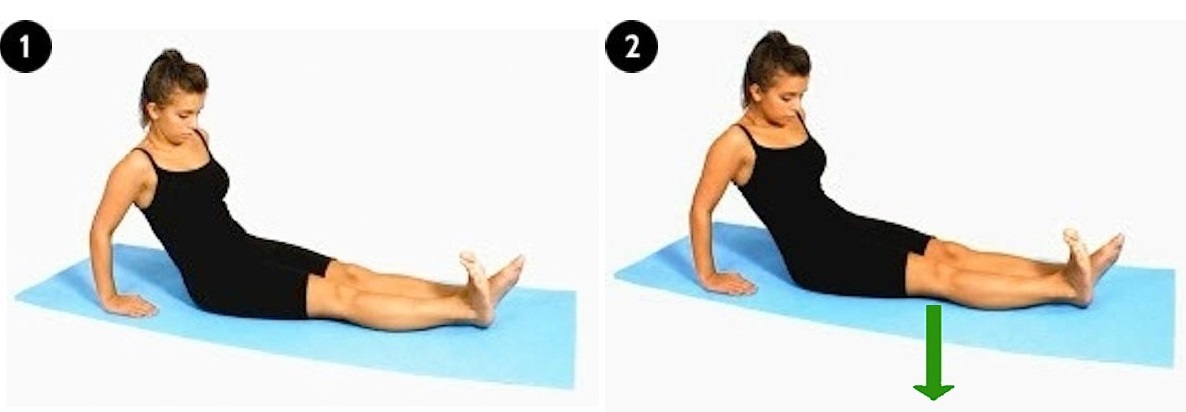 |
(b) Vastus Medialis Exercise
This exercise is very similar to exercise (a). The difference is, roll your leg outwards. The knee will turn out, by 15 – 20 degrees. Then contract your thigh muscles until your heel is lifted from the floor. Make sure your knee remains in contact with the floor. Hold for 5-10 seconds. Repeat 10 times. Do this every waking hour.
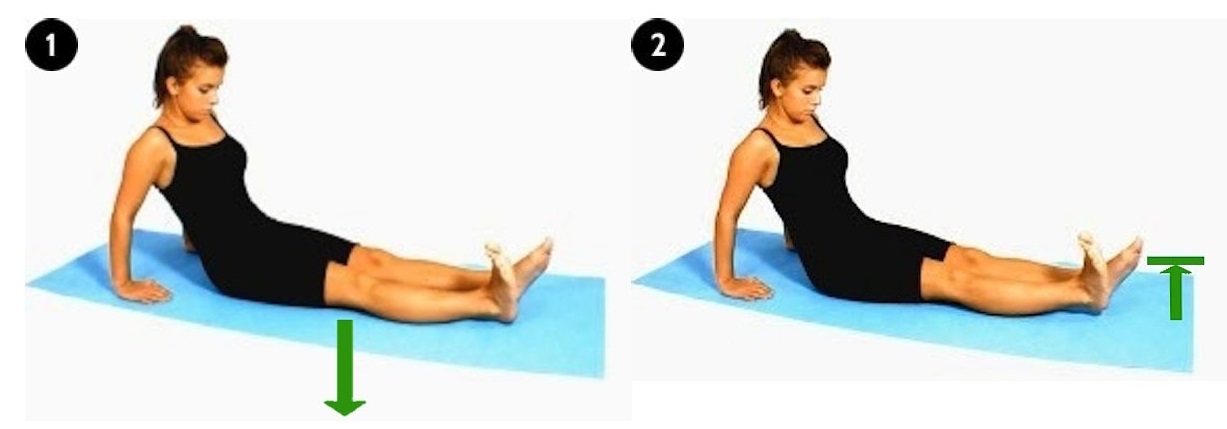 |
(c) Vastus Medialis Resisted Exercise
When your pain further reduces, you are ready to do this exercise. Start by using a ½ kg weight around your ankle. Support your knee on a pillow. Lift your heel away from the floor while keeping your knee firmly pressed into the pillow. Hold for 5-10 seconds. Repeat 10 times. Do this every waking hour. Gradually increase the weight used.
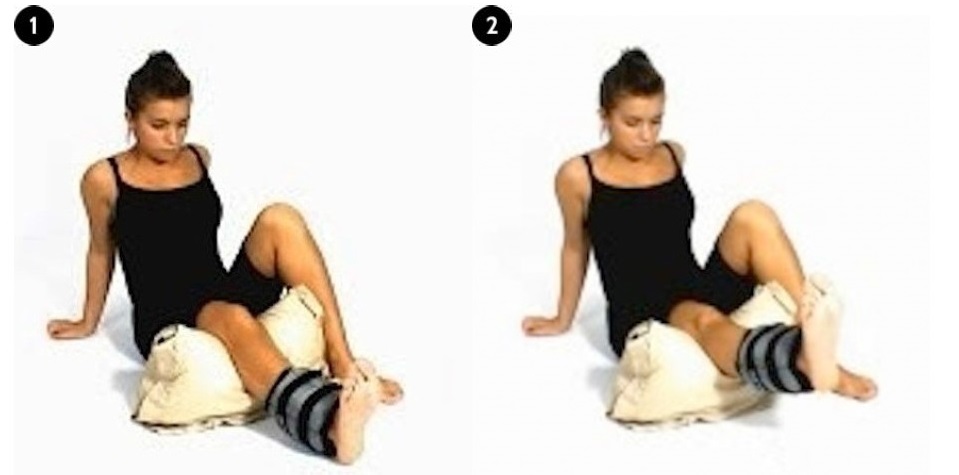 |
(d) Dynamic Quadriceps Exercise
This is also to be done only when your pain has further reduced. Start using a ½ kg weight at your ankle. Sit comfortably in a chair with your thigh supported. Straighten your knee. Hold for 5-10 seconds. Repeat 10 times. Do this every waking hour. Gradually increase the weight used.
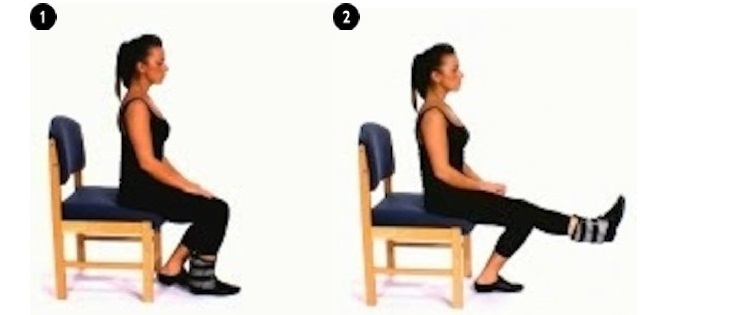 |
(e) Knee Mobilising Exercise
It is important that you prevent stiffness from setting into your knee joint from the very beginning of your recovery.
Lie on your tummy. Slowly bend your knee as much as possible. Hold the bent position for 5-10 seconds. The, slowly straighten it. Repeat 10 times. You can assist with the other leg if needed. Do this every waking hour.
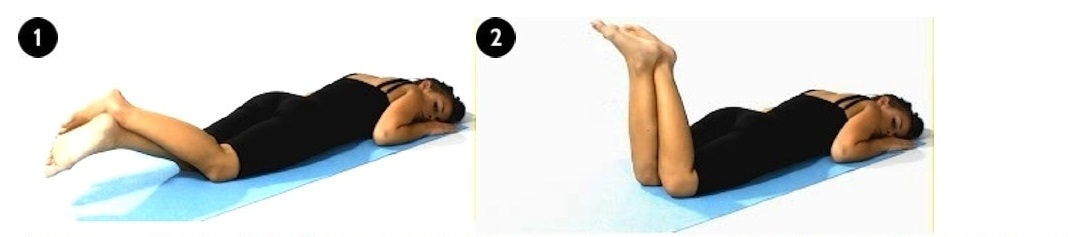 |
|
(Sumber : http://www.exerciseprescriber.com – trial package) |
3. Advance Exercise Therapy
You are advised to see a physiotherapist for a complete rehabilitation programme. Your physiotherapist will examine you and draw up a comprehensive exercise plan customised for you. Usually the focus will be on strengthening your thigh muscles (the quadriceps, especially the vastus medialis).
4. Taping
If you are an athlete, your physiotherapist may decide to tape your knee cap when you return to your sports. This is to prevent recurrent injuries to your knee cap. Taping is also used when performing your exercises.
References
- http://physioworks.com.au/injuries-conditions-1/patella-dislocation
- http://physicaltherapy.about.com/od/sportsinjuries/a/PatellaDislocation.htm
- http://reference.medscape.com/article/90068-treatment#d11
- http://www.sportsinjuryclinic.net/sport-injuries/knee-pain/patellar-dislocation
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer / Translator | : | Nurul Liyana Teong |
| Accreditor | : | Daaljit Singh a/l Harbachan Singh |
| Reviewer | : | Halimah bt. Hashim |







