What is stroke?
Stroke occurs when blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or severely reduced either by a blood clot (ischemic stroke) or burst vessels in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke), depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients causing brain cells. Stroke is the 3 largest cause of death and the most common cause of severe disability in Malaysia.
Prevalence of stroke
There are no national figures on stroke in Malaysia but government hospitals records show about 2,500 deaths and 12,000 stroke discharges every year. The regular age of stroke patients in Malaysia is between 54.5 and 62.6 years.
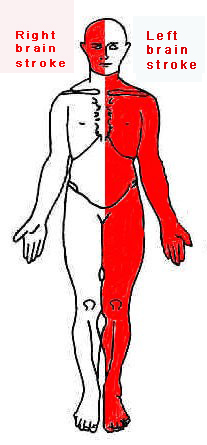
What are the effects of stroke?
The effects of stroke varies and depends on where and how much the brain was injured. A stroke can involve any number of areas and the common effects are:
|
Physical deficits 1. Loss of movement on the opposite side (hemiplegia) of the body where the stroke occurred. Cognitive deficits 1. Disorganized, depressed and poor concentration. Spatial-perceptual deficits 1. Loss of feeling in one side of the body. |
 |
Why is positioning important in stroke patient?
The most common aims of positioning are :
- Modulation of muscle tone.
- Preventing damage to the affected limbs.
- Supporting and stabilizing body segments.
The most recommended positions are as follows :
- Side lying on the non-hemiplegic side.
- Side lying on the hemiplegic side.
- Sitting in an armchair/wheelchair.
Positioning recommended by Physiotherapist
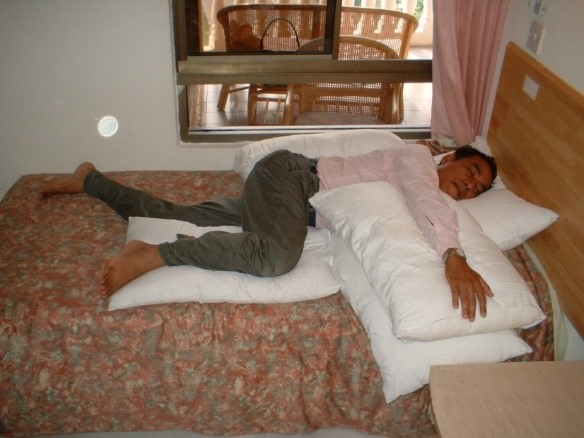 |
Side lying, stroke affected arm supported on a pillow. Hip protracted and bent, knee bent with ankle in neutral position, supported on a pillow. |
Picture 1: Side lying on the non-hemiplegic side
 |
Stroke affected shoulder protracted, arm straight, palm facing upwards. Hips and knees in extension with ankle in neutral positon. |
Picture 2: Side lying on hemiplegic side
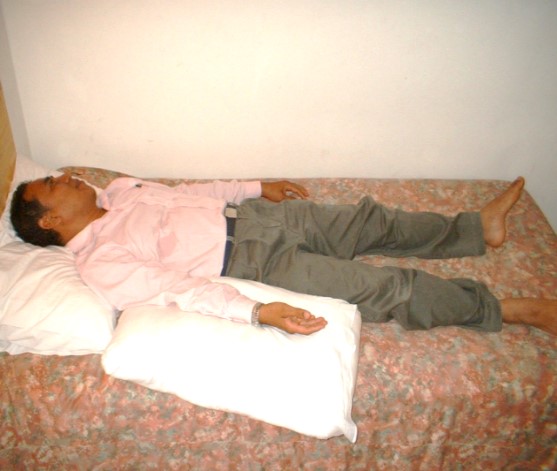 |
Lying face up. Head supported on a pillow. Stroke affected arm supported on a pillow, arm straight, palm facing upwards. |
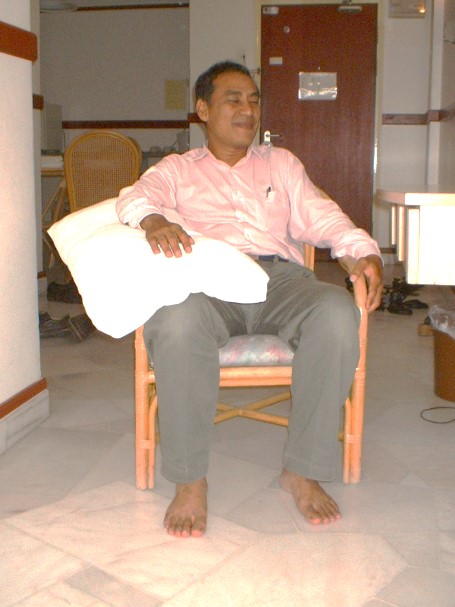 |
Sit well backwards comfortably on the armchair/ wheelchair, trunk upright. If slouch to the stroke affected side, place a pillow under the armpit. Arm supported with shoulder in slight abduction, elbow bent and palms facing down. |
Picture 4: Sitting on arm chair/wheelchair
Support for stroke affected arm apart from positioning with aids
 |
Shoulder brace can be used to prevent the dragging on the paralyzed shoulder muscles causing pain and subluxation. |
Picture 5: Shoulder brace for the stroke affected shoulder.
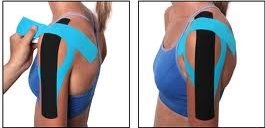 |
Functional taping can also use to provide support for the paralyzed muscles and facilitate better circulation. |
Picture 6: Functional taping for shoulder support.
Patient education and information
You physiotherapist will explain the importance of correct handling when positioning the patients. Care and precautions should be taken to prevent over traction on the stroke affected shoulder causing pain and subluxation. Correct positioning too will prevent pressure sores and increase muscle tone. Contact your nearest physiotherapist for advice and demonstration on the correct positioning.
References
- Burden of stroke in Malaysia, Loo KW et al. Int J Stroke. 2012 Feb; 7(2):165-7.
- Consensus Statement On The Management Of Ischemic Stroke, Academy of Medicine, Malaysia
- Heart & Stroke Foundation 2014
- Positioning for stroke patients: a survey of physiotherapists’ aims and practices. Disability and Rehabilitation Volume 23, Issue 10, 2001
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer / Translator | : | Yew Su Fen |
| Accreditor | : | Ismawi bin Ismail |
| Reviewer | : | Halimah bt. Hashim |







