Protruding teeth is a common problem in both children and adults. Protruding teeth can cause difficulty to close mouth, chewing and speaking, and can make teeth more susceptible to injury, especially during contact sports. Children with protruding teeth may suffer from self-esteem issues.
What are the causes?
Protruding teeth can be caused by genetic (facial), soft tissue, oral habits or crowding of teeth.
- Skeletal facial pattern
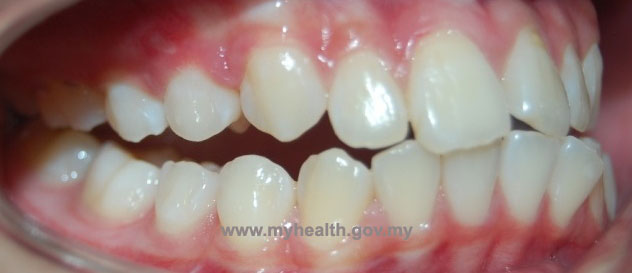
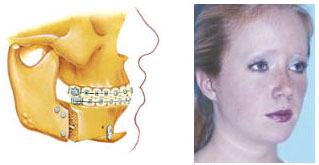
Skeletal facial pattern is genetically influenced. Protruding teeth is usually associated with long upper jaw or short lower jaw (figure 1). Sometimes the upper jaw can grow out of proportion to the rest of the facial structure. The lower jaw may be small in comparison to the upper jaw.
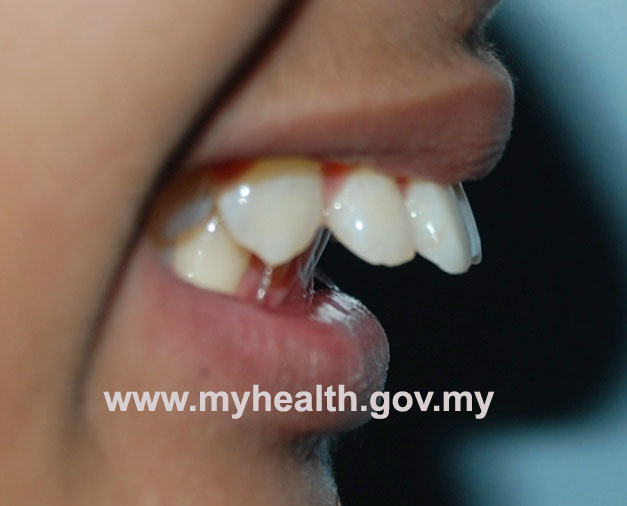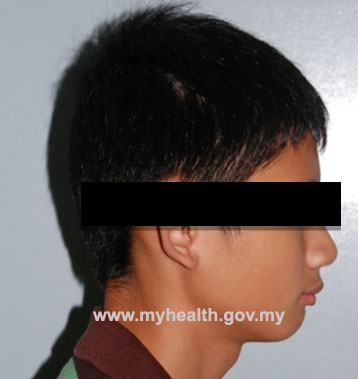
 Figure 1
Figure 1 - Soft tissue factors
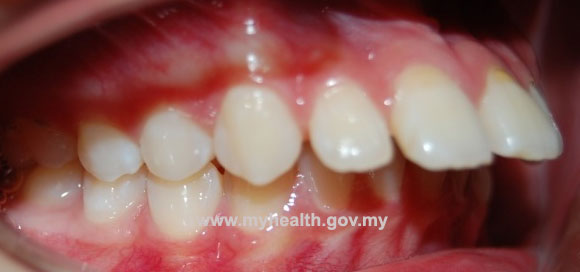
The presence of incompetent lips (upper and lower lip not touching), with failure of the lower lip to control the position of the upper incisors, can be an important cause. If the lower lip is trapped behind the upper teeth (Figure2), the trapped lip will push the upper teeth forward. Occasionally, a strap-like lower lip can cause the lower incisors to incline backward and worsens the protruding teeth. A tongue thrust may also cause incisor to incline forward and causes protruding teeth.
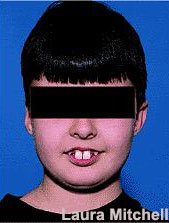
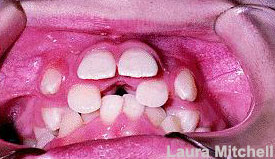 Figure 2
Figure 2 - Habits
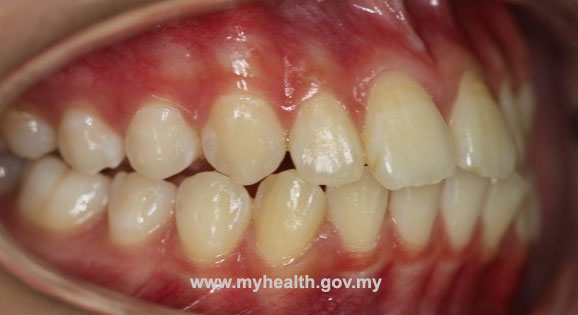
Digit (thumb or finger) sucking can be an important factor causing protruding teeth (figure3).
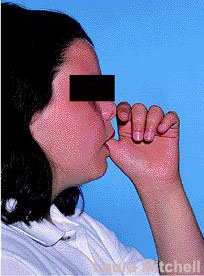
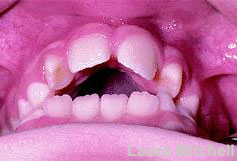 Figure 3
Figure 3 - Local factors
Crowding (overlapping)in the upper arch can cause further forward movement of the upper central incisor and further worsening of protruding teeth. When the teeth don’t have enough space to erupt into, they could begin jutting out (Figure 4).
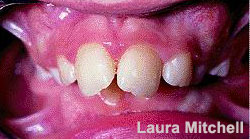
Figure 4
| Causes of protruding teeth | |
|---|---|
| Skeletal facial pattern |
|
| Soft tissue factors |
|
| Habits |
|
| Local factors |
|
What are the benefits of fixing the protruding teeth?
Benefits of treatment include:
- An improvement in teeth and facial appearance
- A reduction in the risk of teeth injuries
- Relief of a deep traumatic bite (whereby the lower teeth touches and damages the upper gums)
What are the treatments for protruding teeth?
The treatment of protruding teeth depends on the patient’s motivation, age, severity of skeletal discrepancy and the facial profile.
Teenager
Mixed dentition (Both deciduous and permanent teeth present)
Await permanent dentition. No treatment needed.
Early Permanent dentition
-
Mild case
It can be treated with fixed appliances by upper incisor retraction (camouflage treatment, Figure 5). Fixed appliance treatment usually takes 18-30 months to complete depending on the severity of the condition.
Before fixed appliances are placed, space often has to be created for the relief of crowding and upper incisor retraction. If necessary, upper premolars can be extracted to provide space.

Figure 5 -
Moderate case
Moderate cases are often best treated with functional appliances to reduce severity of protruding teeth, followed by fixed appliances for alignment.
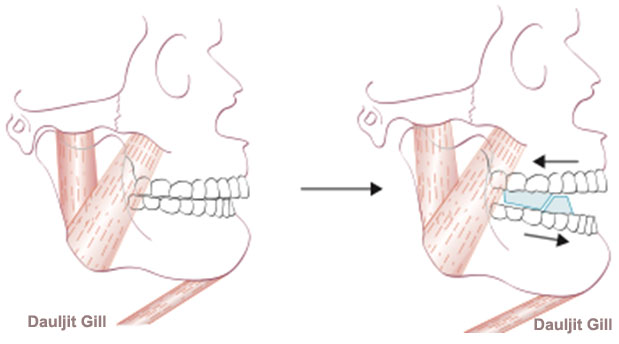
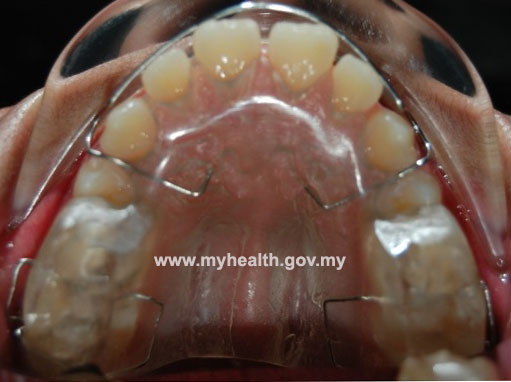
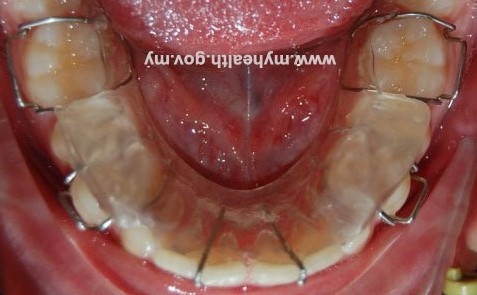
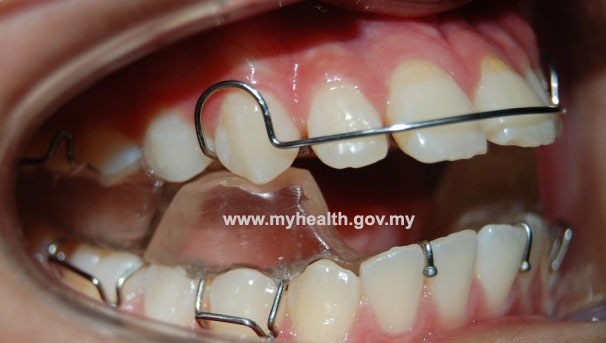
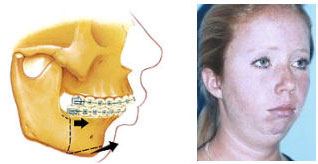
Functional appliance is a removable brace that works on the upper and lower teeth at the same time (figure 6). It is a growth modification method by attempting restraint of upper jaw’s growth, whilst encouraging lower jaw’s growth, or by a combination of the two (Figure 7). Headgear (figure 8) can be added to restrain growth of the maxilla further. Functional appliance treatment usually can be completed in about 9-12months (figure 9).
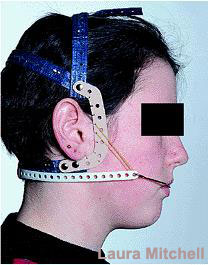 Figure 6 Figure 7Figure 8Figure 9
Figure 6 Figure 7Figure 8Figure 9 - Severe case
Severe case is best managed at the completion of facial growth with a combination of braces and jaw surgery (figure 10.1 and 10.2).
Figure 10. 1 Before surgery
Figure 10. 2 After surgery
Photo source : http://www.augersmiles.com/Treatment/OrthognathicSurgery.aspx
As growth in adult patient has ceased, so jaw growth modification is not feasible. Adults with protruding teeth usually need extractions of teeth and fixed appliance treatment. In severe cases, jaw surgery may be necessary to change the placement of the jaw. Otherwise treatment should be given to alignment (straightening) only or partial correction of protruding teeth.
|
Age
|
Stage
|
Severity | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Teenager | Mixed dentition | No treatment needed | |
| Early Permanent dentition | i) Mild case | Fixed appliances with extractions | |
| ii) Moderate case | Functional appliances followed by fixed appliances | ||
| iii) Severe case | Combination of fixed appliances and jaw surgery | ||
| Adults | Fixed appliances with extractions, or combination of fixed appliances and jaw surgery depending on severity of case |
Conclusion
Early treatment should be started at the optimum age when patient is still growing to obviate the need for complicated treatment later.
References
- Gill DS. Orthodontics: At a glance. 2008. Wiley-Blackwell Publishing.
- Laura Mitchell. An Introduction to Orthodontics 4th Edition. 2013. Oxford University Press.
| Last Reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Mah Eng Ching |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Arjunan a/l Muthusamy |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Hjh. Rashidah bt. Dato’ Hj. Burhanudin |