What are refractive errors?
Light travels through the cornea (clear transparent part of the eye) and the lens before falling on the retina (the retina is the nerve layer that lines the back of the eye). The eye needs to bend (refract) the light rays so that the image can be focused sharply on the retina. In a person who has refractive error, the eye does not bend (refract) the light properly. This results in blurred images.
Types of refractive errors
- Myopia
It is the most common type of refractive error among children and young adults. It tends to run in families. It occurs when the cornea is curved too much or the eyeball is too long. The light is focused in front of the retina rather than precisely on the retina.
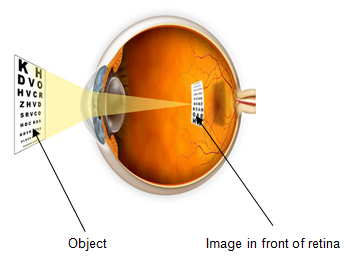 |
| Diagram showing image in myopic eye |
It is often discovered when children enters schools, as early as 6 years old. During the teenage years, (when the body grows rapidly) myopia may become worse. However between 20-40 years of age, the degree/power of short sightedness stabilizes.
- Hyperopia
This occurs when the cornea is curved too little or the eye is shorter than normal. This results in the light focusing beyond the retina. Babies and young children tend to be slightly hyperopic. This lessens as the eye grows and becomes longer.
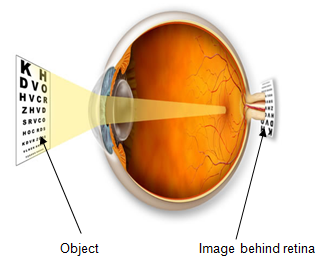 |
| Diagram showing image in hyperopic eye |
- Astigmatism
It occurs when the cornea is unevenly shaped and it bends the light in different directions. It may occur in combination with other refractive errors.
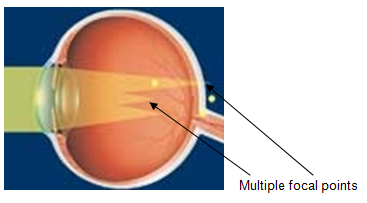 |
| Diagram showing image in astigmatic eye |
What are the symptoms?
Myopia (Near sightedness)
- Near objects are seen clearly whereas distant objects are blurred.
- Children may squeeze their eyes when trying to see distant objects.
- School children are unable to see the blackboard clearly.
- Children may hold their books too close to the face while reading.
Hyperopia (Far sightedness)
- Near objects appear blurred whereas distant objects are seen well.
- Children have difficulties with near work such as reading and writing.
- Children may complain of eye strain and headache while trying to read for long hours.
- Affected children may have squints.
Astigmatism
- Near and distant objects appear distorted or blurred.
- Children often complain of eye strain and headache.
- The blurred vision occurs more in one direction than another.
- Children with astigmatism typically see vertical lines more clearly than horizontal lines and sometimes the reverse.
Besides poor vision what are other potential problems?
- Eye strain and headache.
- Impaired safety : riding a bicycle without correction of significant refractive error may endanger the child and others.
- Inability to perform tasks well may result in reduced quality of life.
- Severe or high myopia increases the risk of detachment of retina and macular degeneration, which are serious eye disorders that may lead to blindness.
- Uncorrected refractive error in children may lead to lazy eye (amblyopia).
What is the treatment?
- Eye glasses or contact lenses are the most common methods of correcting refractive errors.
- In children, eye glasses are preferred.
- Older children may be allowed to wear contact lenses depending on his/her ability to insert and remove lenses properly. They should also take them out as required and clean them as recommended by the doctor.
- Surgery to correct refractive errors is not recommended since the child is still growing except in certain circumstances.
| Last reviewed | : | 26 April 2012 |
| Content Writer | : | Dr. R. Sukumar a/l Rajaretnam |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Salmah bt. Othman |







