Introduction
Stroke is a condition that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted. The brain functions as the main control center of the body, helping to execute decisions of our thoughts and action. In addition, the brain also controls automatic functions like breathing.
The brain needs constant supply of blood with oxygen and nutrients. Once the blood vessels in the brain ruptures or is occluded, the blood supply will be terminated. The brain cells incidentally will be deprived of oxygen and nutrients.
Once the brain cells start to die, the damage will immediately affect your senses, speech and language understanding. One side of the body may be paralyzed and execution of movement might be a problem. Stroke may also affect behavior and memory.
 |
Physiotherapy treatment objectives :
- Accelerating the pace of recovery of the neuromuscular system like voluntary limb movement, balance, coordination of movement and ability to walk.
- Restoring functional activities to ensure optimal mobility and independence (independent optimal functional recovery).
- Prevention of complications such as :
a) Pressure sores
b) Foot Drop
c) Contracture
d) Respiratory Complications
Sign and Symptom
Strokes may happen without warning. However, some individual exhibits some obvious warning signs. By recognizing these signs and take immediate action like attaining immediate medical attention, the impact of stroke can be minimized effectively. Main warning signs :
- Sudden weakness or numbness perceived over one side of the body.
- Drooling and slurred speech
- Blurring of vision in one or both eyes
- Sudden difficulty in speaking (or slurred speech) or understanding conversation
- Dizziness, loss of balance, confusion
- Severe onset of headache
- Nausea or vomiting
Complications
The outcome of a stroke depends largely on which part of the brain is affected and the severity of that damage. For some people, the effects are relatively minor and may take a shorter time to recover. Others may experience more severe form of impairment or disability in a long term. Among the complications of stroke are as follow :
Physical disability after stroke
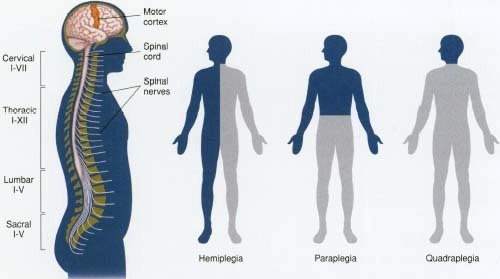
- Loss of movement or abnormal movement patterns in the body (hemiplegia). Because the right side of the brain controls the left side of the body (and vice versa), hemiplegia occurs in the body as opposed to the location of the stroke.
- Weak coordination
- Randomized abnormality.
- Difficulty speaking and understanding, as well as reading and writing.
- Unable to control bowel movement.
- Partial loss of vision.
- Unable to swallow.
Cognitive deficits
- Becoming overly vigilant, anxious and panic.
- Easily depressed, unable to control his emotions.
- Low concentration in learning new skills.
- Unable to understand speech.
Lack of space perception – spatial awareness
- Unable to guess the distance , size, position
- Loss of feeling in the body
- Loss of body image.
Other complications such as :
a) Pressure sores
b) Foot Drop
c) Contracture
d) Respiratory Complications
Prevention
- Take adequate amounts of nutritious foods such as fruits and vegetables.
- Check blood pressure regularly.
- Maintain an ideal body weight because obesity is one of the causes of stroke.
- Do active physical activity for at least 2 times a week. Example: Brisk walk, Tai Chi, stretching exercises and active exercises.
Rehabilitation
- Program exercises for stroke patients
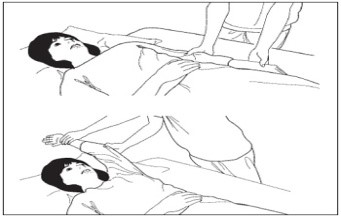
Passive exercise to maintain joint range
Exercise for the upper limb
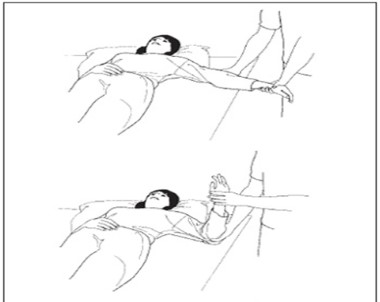
Bend and extend the elbow. 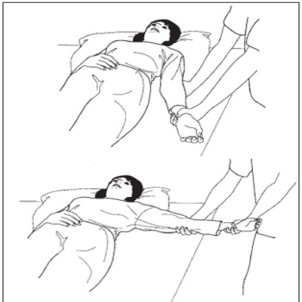
Rotational movement of the shoulder joint 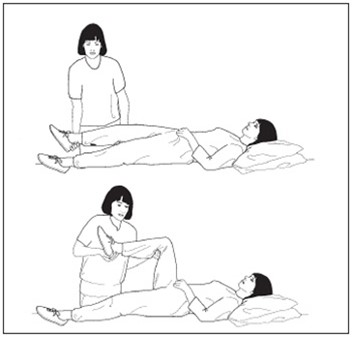
Bend and straighten the knee. 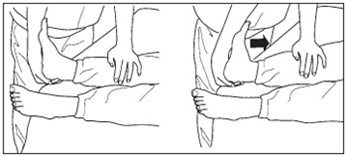
Bend the ankle joint - Way right position stroke patients
-
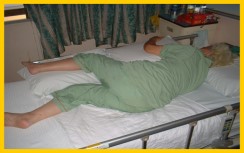
Lying on the unaffected side
• Support the affected limbs on pillows
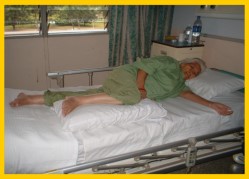
• Lying on the affected side
• Place the affected arm in a straight position (as in the picture)
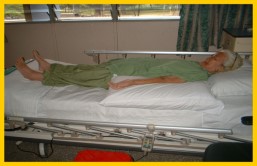
• Place the affected upper limb on a pillow - Shifting and Lifting
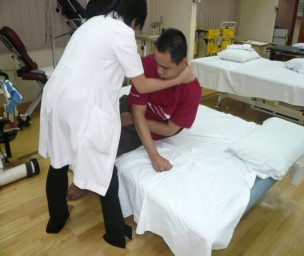 |
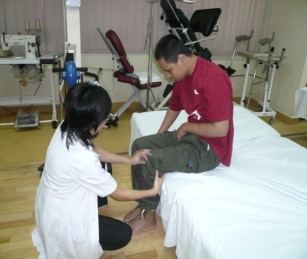 |
Roll to the side. With minimal help from the care, push your body up to sitting position and place both feet on the floor. |
References
- Patricia M. Davies, 1990, Right in the middle, Springer – Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
- Patricia M. Davies, 1994, Steps To Follow, A Guide to the Treatment of Adult Hemiplegia, Springer – Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
- Standard Operating Procedures, Treatment of Neurology.
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer / Translator | : | YBhg Datin Hjh Asiah binti Mohd Hashim |
| Accreditor | : | Haironi binti Ismail |
| Reviewer | : | Halimah bt. Hashim |







