The ultrasound scan is an important part of the IVF and IUI programme, where it gives us information about the lining of the womb (uterus) and the number and size of follicles, and any existing pathology, such as cysts or fibroids, which will help your doctor to decide about your next stage of treatment. Your treatment in the Fertility Clinic will involve a number of ultrasound scans.
All the ultrasound scans are internal (transvaginally) and are not painful. It involves a specially shaped ultrasound probe (slightly bigger than a tampon) being inserted into the vagina. Some patients may find it a little uncomfortable, but it is not as bad as a smear test! The probe is cleaned and covered before use for each patient.
The ultrasound scans are performed transvaginally with an empty bladder. It provides a better image of your pelvic organs so we can get the maximum amount of information. Please go to the toilet before your scan.
The examination will take less than 10 minutes and is similar to having a Pap smear test. It is not painful. A probe is inserted into your vagina and pictures of the womb and ovaries can be seen on the screen.
You will be asked to undress from the waist down, including your underwear, and lie on the ultrasound couch with a pillow under your bottom. (You may find it more convenient to wear clothing that is easy to remove). You will be asked to bend your knees, then the doctor carefully insert the ultrasound probe into the vagina.
You may have at least three scans during the course of your treatment, depending upon the treatment you require, the medication you are taking and how you respond to the drugs.
The first scan usually will be performed during your period – please don’t worry about this. This scan is called a ‘baseline’ scan and is to document any pathology within the uterus or ovaries before the treatment begins.
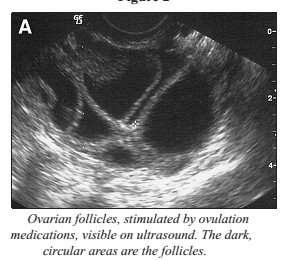
For IVF patients during treatment, the second scan is one week later and then the scans are repeated at intervals to check for follicles. When the follicles get bigger, the doctor measure them. This can sometimes take a while depending on how many follicles there are. The doctors perform three different measurements on each follicle and work out the average diameter in millimetres.
Ultrasound in follicular tracking
Fertility medications (to stimulate the follicles to grow) generally take eight to 14 days. The dose of the medications might be adjusted in an effort to improve follicular development. When the follicles are ready, Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is given. The hCG (Profasi®, Novarel®, Pregnyl®, Ovidrel®) is a hormonal drug that stimulates the final maturation of the oocytes. It replaces the woman’s natural LH surge and causes the final stage of egg maturation so the eggs are capable of being fertilized. The eggs are retrieved before ovulation occurs, usually 34 to 36 hours after the hCG injection is given. Usually, the hCG injection is given when four or more follicles have grown to be 18 to 20mm in size and your estradiol levels are greater than 2,000pg/ML.
Determining the proper day for hCG administration is critical. The time of the injection determines when the egg retrieval will be scheduled. Some protocols using GnRH antagonists use GnRH agonists to trigger the final maturation of oocytes.
Ultrasound in follicle aspiration
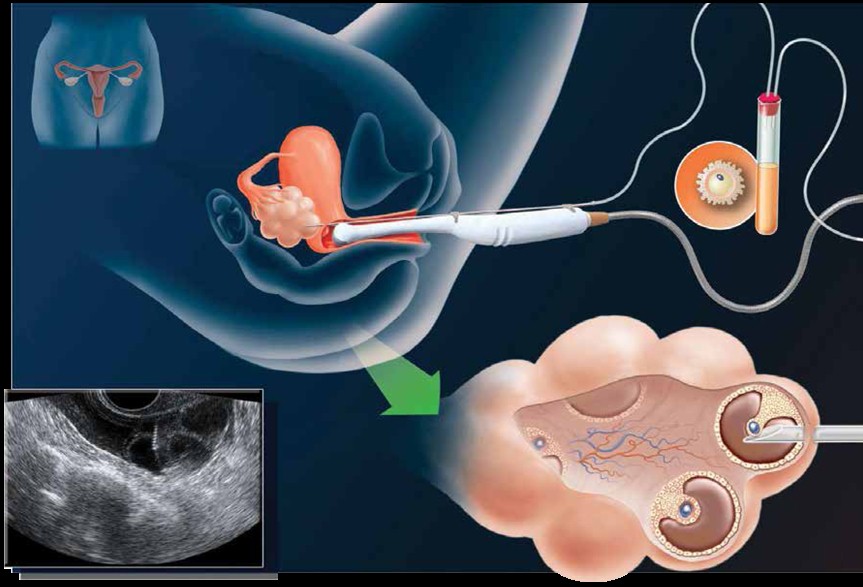
Egg recovery is carried out under sedation. The eggs are recovered by needle aspiration under vaginal ultrasound guidance.
An anaesthetist administers intravenous medications (sedatives and pain relievers) in order to minimize the discomfort that may occur during the procedure. Most patients sleep through the procedure. A transvaginal ultrasound probe is used to visualize the ovaries and the egg-containing follicles within the ovaries. A long needle, which can be seen on ultrasound, can be guided into each follicle and the contents aspirated. The aspirated material includes follicular fluid, oocytes (eggs) and granulosa (egg-supporting) cells. The doctor will collect the oocytes and follicular fluid into a test tube and the embryologist will search the follicular fluid and locate the oocytes using a microscope.
Ultrasound in embryo transfer
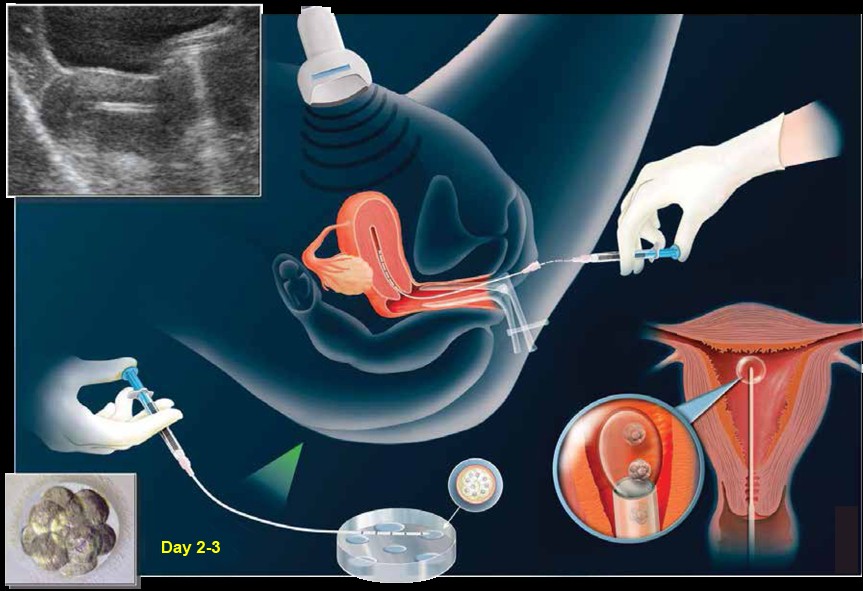
The embryo transfer procedure is usually performed three to five days after oocyte retrieval. The doctor, under ultrasound guidance, will pass a catheter gently through the cervix into the uterus and deposit the embryos into the uterine cavity along with an extremely small amount of fluid. You may be asked to fill up your bladder for this procedure. This is to ease the doctor during embryo transfer. This procedure usually does not require anaesthesia, and the patient usually leaves the office after a brief recovery period.
Ultrasound in IVF pregnancy
Confirming pregnancy after IVF can be very emotional time for the patients. It should be carried out between week 5 and 7 of pregnancy, therefore between 3 and 5 weeks after embryo transfer. To calculate the pregnancy after IVF, we always set a theoretical last menstrual period date 14 days before egg retrieval.
Exactly one month after the embryo transfer is a great time to carry out the ultrasound scan and see clearly if the pregnancy is progressing or not. If this is done sooner, we can create confusion and uncertainty since most of the time it will not be conclusive.
The ultrasound must be done vaginally. This shows the images more clearly, and it is more precise in showing that everything is evolving correctly. We know that carrying out the ultrasound this way does not negatively affect the pregnancy.
It is important to do an ultrasound in the 6th or 7th week because we can confirm that the pregnancy is in the uterus, and rule out ectopic pregnancy (found outside the uterus). We can see if it is a single or a multiple pregnancy and it allows us to evaluate whether or not the pregnancy evolution is as it should be. If it is not evolving well, it can give us an idea as to why. The foetal heartbeat tends to appear around week 6.
Ultrasound in IUI
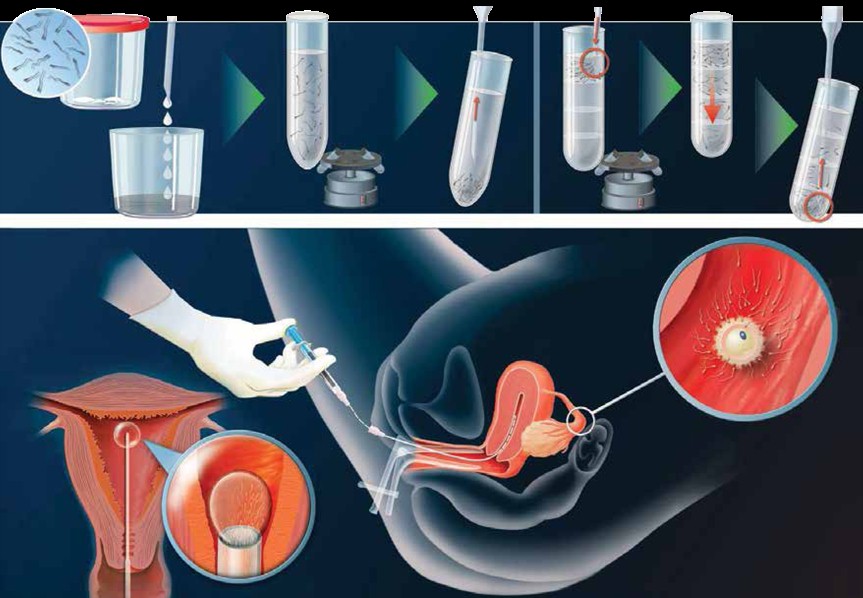
The ultrasound procedures in IUI are similar to IVF. However, in IUI the washed sperm of your husband is replace in to your womb. The doctor, under ultrasound guidance, will pass a catheter gently through the cervix into the uterus and deposit the washed sperm into the uterine cavity.
N.B.
Endometrium is the lining of the womb and the doctor measure this each time you are scanned. It is thin when you are on your period and thickens in response to the medication.
Follicles are in the ovaries and should contain an egg. The follicles grow in response to the medication. The follicles need to be a certain size before you are ready to go to theatre for egg retrieval. (The eggs are invisible to the naked eye and cannot be seen on the scan.) The IVF doctor will decide when your egg retrieval will be.
Cysts are little sacs of fluid which sometimes seen on the baseline scan.
Hydrosalpinx means fluid in the fallopian tubes, sometime seen during the treatment, it can be a side effect of the medication or associated with blocked fallopian tubes.
Fibroids are thickened lumps of muscle within the muscle of the uterus and the doctor measures these and check whether they are pressing on the cavity of the womb.
Polyps are benign growths that can be found on the lining of the womb and may cause problems with the embryo implanting easily.
References
1. The role of ultrasound in female infertility management., Hackelöer BJ et al Ultrasound Med Biol. 1984 Jan-Feb;10(1):35-50.
2. Ultrasonic study of follicular maturation, ovulation and development of corpus luteum during normal menstrual cycles. Lenz S. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1985;64(1):15-9.
| Semakan akhir | : | 28 August 2015 |
| Penulis/ Penterjemah | : | Dr.Hj.Mohamed Hatta bin Mohamed Tarmizi |
| Akreditor | : | Dr. Noraihan binti mohd Nordin |