Introduction
National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA), Ministry of Health Malaysia is formerly known as the National Pharmaceutical Control Bureau (NPCB). Under the Control of Drug and Cosmetic Regulatory 1984, NPRA is the only regulatory agency in Malaysia that acts as the secretariat to the Drug Control Authority (DCA).
The primary role of NPRA is to ensure that pharmaceutical substances, traditional medicines and cosmetic products are safe and quality to be used by the Malaysians.
To achieve this objective, NPRA has implemented a regulatory system for medicinal products which involves several processes including product registration (pre-registration), licensing (importers, manufacturers and wholesalers premises) and post-marketing surveillance for registered product (post-registration). Product quality control process is one of the significant elements in these processes in ensuring the safety levels of medicinal products.
Evaluation of Products Safety Level
Analytical data analysis and laboratory testing are the main activities in product quality control process in NPRA. Evaluation and laboratory tests are conducted in accordance with the registration requirements and also depending on product categories such as pharmaceutical or traditional medicinal products. The registration requirements have been detailed in the product registration guidelines known as Drug Registration Guidance Document (DRGD). Product registration process conducted in NPRA is as shown in Chart 1.
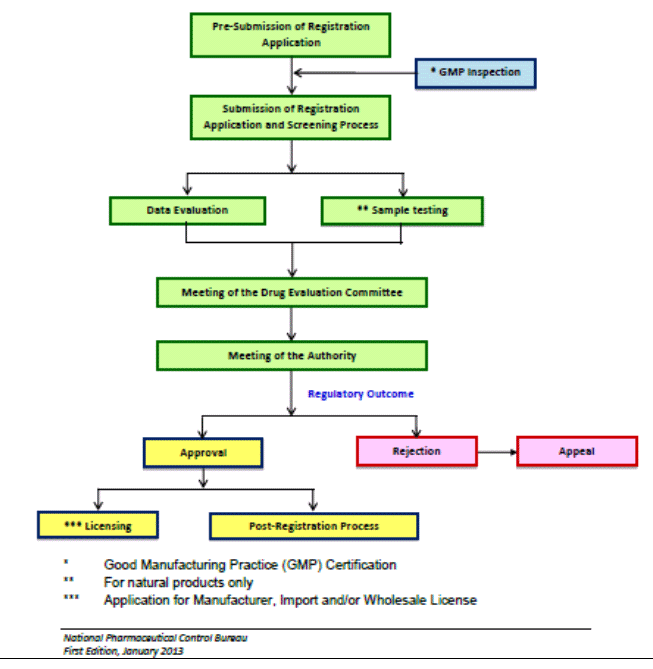
Chart 1: Product registration work processes
Data evaluation involves reviewing documents submitted by applicant which include product information (indication, stability data, label and storage requirement), laboratory testing procedures used, product’s analytical validation data and etc.
Routine test carried out on pharmaceutical product in post-registration activities are as follows:
- Physical tests including appearance, pH, weight uniformity of dosage units, and melting point test.
- Quality tests such as identification test and assay of active ingredient, related substances and impurity test.
- Dosage performance tests such as disintegration and dissolution test.
- Safety tests for example microbial contaminant test (fungus and microbes)
Routine tests conducted on traditional medicinal product in pre and post-registration activities are as follows:
- Physical tests for example appearance, pH and weight uniformity dosage units test.
- Dosage performance tests such as disintegration test.
- Safety tests such as microbial contaminant test (fungus and microbes) and heavy metals analysis (mercury, lead, cadmium, and arsenic).
- Adulterant’s screening tests. (Refer to Table 1).
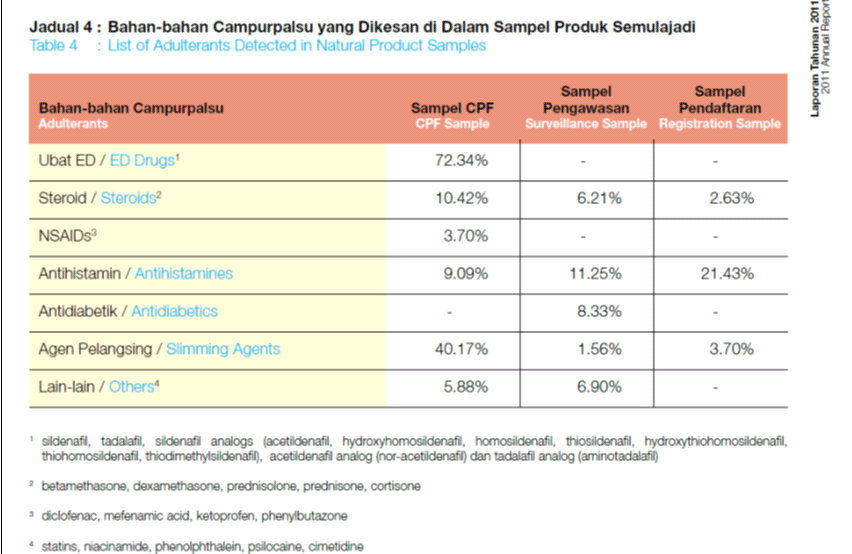
Table 1: NPCB Annual Report Year 2011, indicates antihistamine drugs, steroids and slimming agents are substances often adulterated in traditional medicine products.
Common Adulterated Traditional Products
Generally, traditional medicinal products with claims as listed below or any products received from consumer’s complaint will be subjected to adulterant screening test.
- For men’s health
- For muscle and joint pains
- For slimming
- For cough and cold
Statistical report shows, from a total of 853 products screened for adulterated substances, only 2% of the screened products were found to be adulterated during pre-registration process, 12% were found to be adulterated are registered products received from surveillance activity. The remaining 86% found contaning banned substance are unregistered product received from Pharmaceutical Services Division, Ministry of Health. Most products found containing banned substance such as scheduled poisons are categorized under health supplements and beverages.
Examples of steroids used as adulterant are betamethasone, dexamethasone, prednisolone, prednisone and cortisone. These drugs are often used to treat muscle and joint pains. Prolonged use of steroid without professional supervision may lead to muscle weakness, bone loss, increased blood sugar, high blood pressure and Cushing’s Syndrome.
Examples of antihistamines used as adulterant are promethazine, chlorpheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine and ephedrine. These drugs commonly used to treat colds. Any usage of antihistamine exceeds the permitted dosage will lead to adverse effects such as hallucinations, stroke and low blood pressure.
Examples of male’s sex stimulants used as adulterant are sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil and its analogues groups. These are prescribed items which require prescription and doctor’s supervision . Serious adverse events such as loss of vision and hearing, low blood pressure, risk of heart attack and stroke may occur if taken without proper dosage and monitoring from a doctor.
Examples of antidiabetic used as adulterant are metformin and glibenclamide which are mainly used to control blood sugar. The use of these substances without a doctor’s supervision will lead to low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) and decreased kidney function.
Examples of slimming agents used as adulterant are sibutramine and fenfluramine. Uncontrolled use of slimming agent can cause undesirable effect to cardiovascular system.
Registration status of a product that is found adulterated will be revoked and no longer allowed to be imported, manufactured, distributed and sold in the Malaysian market.
Check product registration status as the following:-
- Identify the registration number on the product label. Each medicinal product registered with the DCA will be given a registration number that begins with ‘MAL’, followed by eight (8) digits and ends with a letter(MAL 2013XXXXT).
- Apart from registered number, every product registered with the DCA will also be given a hologram sticker. Check the presence of hologram sticker on the product label. The authenticity of the hologram can be determined by using Meditag decoder which is available in retail pharmacy outlet.
- Go to NPRA official website, http://npra.moh.gov.my Press ‘Quest Products Search’ button for further information.
Conclusion
DCA will ensure all registered product are safe, effective and good quality through scrupulous evaluation of scientific data and laboratory testing on all products before they are marketed alongside with an ongoing monitoring activity by post marketing surveillance activity after products are made available in the market.
All parties, especially manufacturers, importers and consumers should play a role in ensuring medicinal products which are marketed in Malaysia are good quality, effective and safe to use.
References
- BPFK, (2013).Drug Reference Guidance Document (DRGD), Section A : General Overview, pg 26, First edition, revised August 2013
- BPFK, (2013).Drug Reference Guidance Document (DRGD), Section C : Quality Control, pg 89 -102 First edition, revised August 2013
- BPFK, (2013).Drug Reference Guidance Document (DRGD), Appendix 5 : Guideline on registration of natural products, pg 240 – 312,First edition, revised August 2013
- BPFK, BPFK Annual Report 2011, Pengujian Sampel, ms 48 – 53.
- Pembatalan Pendaftaran Produk Semulajadi (Tradisional) Atas Isu Campurpalsu http://portal.bpfk.gov.my/index.cfm?&menuid=117&parentid=116 retrieved 7th Oct 2013
- Ubat Tradisional & Komplimentari https://myhealth23.primuscore.com/v2/index.php/my/ubat-a-anda/ubat-tradisional/ubat-tradisional-a-komplementari)
| Last Reviewed | : | 19 October 2017 |
| Translator | : | Maisara bt. Abd Rahman |
| Accreditor | : | Munira bt. Muhammad |







