What is Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a medical condition of the spine whereby the spine of an individual curves to the right or left. It is not a systemic disease. The word scoliosis is a Greek word which means crooked.
The spinal vertebrae will not only curve to the sides but it will also rotate on its vertical axis. Increased curvatures to the front and back can also accompany. This 3 dimensional changes will bring about negative cosmetic effects and a possibility of health complications of the individual concerned. This problem was identified thousands of years ago, during the times of Hippocrates. Generally these cosmetic changes will not jeopardize the health and functional status of an individual. If however the curvature is too marked, the heart and lungs can be compressed by the deformed ribs. This will bring about a constraint in the cardiovascular function.
Scoliosis can be classified into two main types:
i) congenital, whereby the deformity of the spine already exists when the child is born, and
ii) idiopathic, which means of an unknown cause. Scoliosis can also present itself as a complication of neurological conditions (abnormalities of the nervous system).
80% of scoliosis cases fall into the category of Adolescence Idiopathic Scoliosis. The spine curves to such an extent that it becomes sufficiently large to be seen. Generally it worsens over a period of 2 to 3 years. This happens during at the time of growth spurt at age around 9 years for girls and 12 for boys. The imbalanced growth of the spine causes scoliosis. This condition is more prevalent in girls.
Signs and symptoms
- Uneven shoulder level
- Prominent hip to side
- A rib hump due to the deformed ribs
- Imbalanced musculature
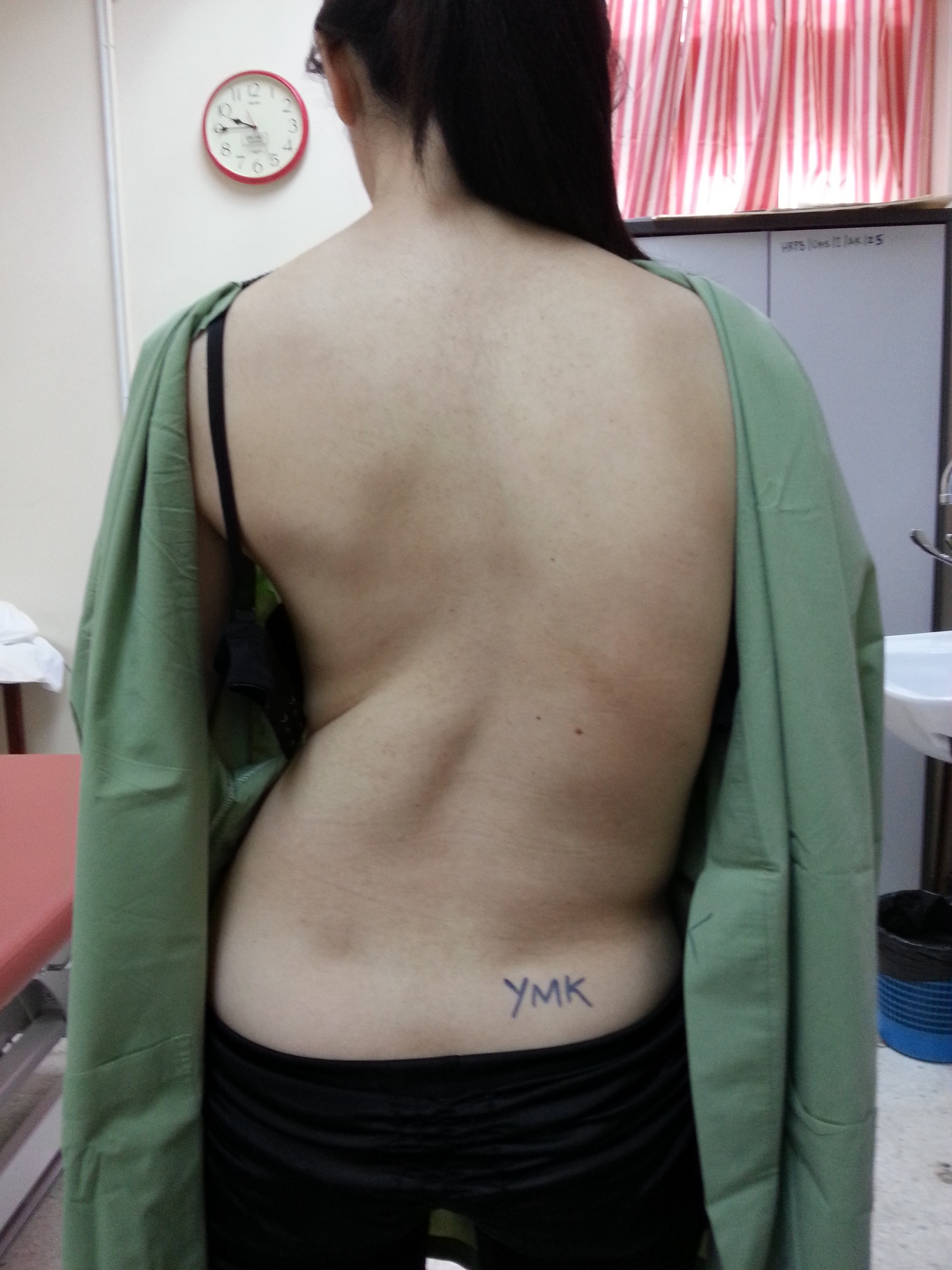
Scoliosis (Image, courtesy of the author)
Diagnosis
Postural screening of school children is very much encouraged. The individual is screened with adequate exposure. The individual is asked to bend forward with both palms between the knees. If a hump is noted on one side of the chest or low back, or if one scapula is higher, then an X-Ray should be taken to confirm if it is scoliosis. A scoliometer can be used to determine it too. A reading of more than 5 degrees must be investigated further with an X-Ray.
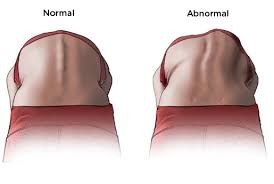
Google Images
An X-Ray should be taken from the side (Lateral View) and from the back (AP View)
X-Ray of an individual with scoliosis taken from the back will show the spine to be in a shape of “C” or “S”.
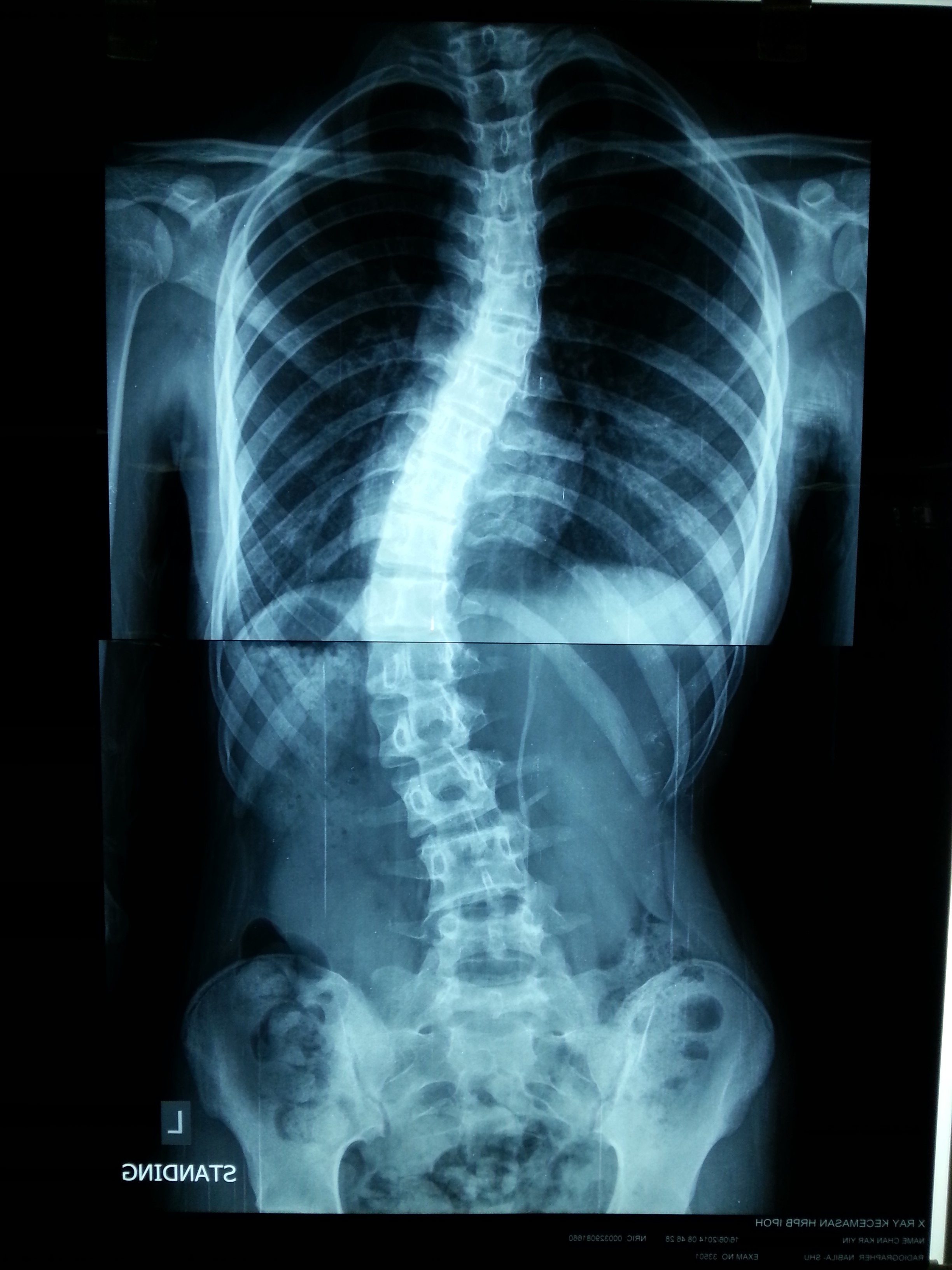 |
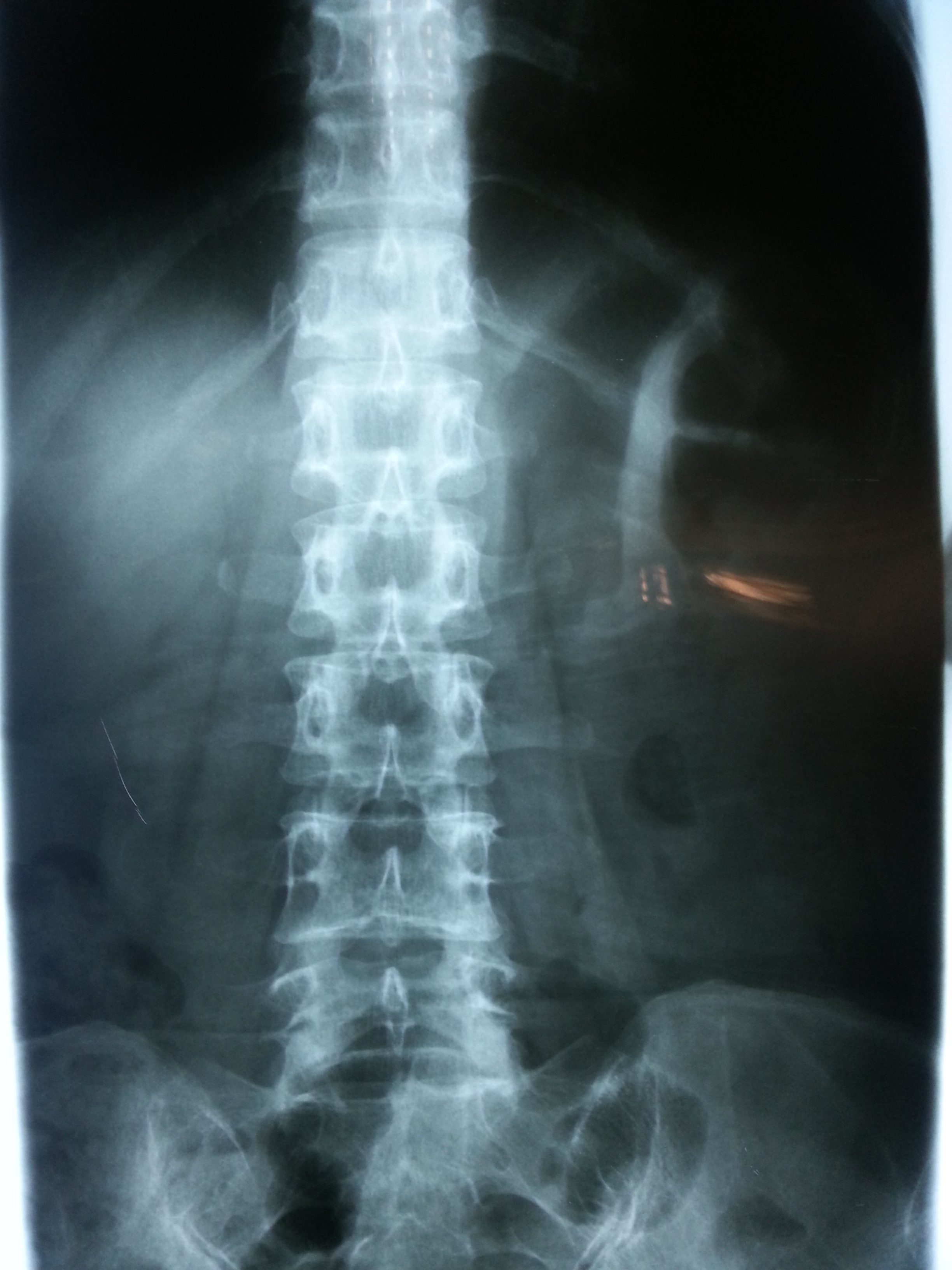 |
|
Scoliotic Spine (Courtesy of the author) |
Normal Spine (Courtesy of the author) |
Treatment
The Schroth exercise technique from Germany has been demonstrated to be very effective for the rehabilitation of the scoliotic patient. The physiotherapist will prepare the exercise programme for the individual based on the existing deformity of the spine. The exercises are intended to stretch the tight or short muscles and strengthen the weak muscles.

Schroth exercises from Google Images
Cases with a Cob’s Angle of more than 20 degrees are recommended to use a customised Brace. Braces are worn like hard jackets to maintain a corrected body posture
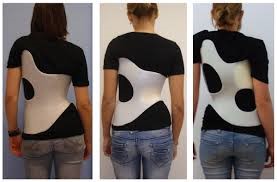 |
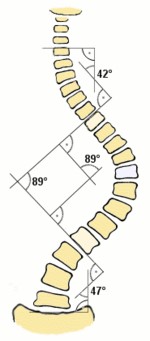 |
| Brace for Scoliosis from Google Images | Cobb’s Angle |
Surgery will be proposed for those with a Cobb’s Angle of more than 45 degrees.
Reference
- Google Images
- Images by courtesy of the author
- Lehnert-Schroth C (2007). Three-Dimensional Treatment for Scoliosis: A Physiotherapeutic Method for Deformities of the Spine. Palo Alto CA: The Martindale Press. pp. 1–6. ISBN 0-914959-02-6.
- Wikipedia the Free Encyclopedia
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer / Translator | : | Daaljit Singh a/l Harbachan Singh |
| Accreditor | : | Se To Phui Lin |
| Reviewer | : | Halimah bt. Hashim |







