Introduction
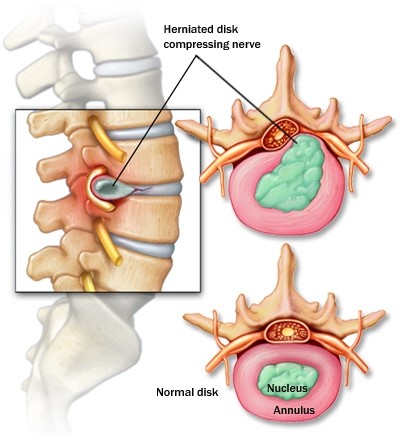
Slipped Disc of spine is also known as Prolapsed intervertebral disc (PID). Slipped Disc is the displacement of nucleus pulposus from the center of the disc which might cause body limbs become numb/weak.
Slipped Disc at the spine is one of the common diagnosis among back pain patients. Slipped Disc might be influenced by degenerative changes of the spine disc due to mechanical, trauma, nutrient and genetic factors.
Slipped Disc at the spine usually occurs due to factors which leads to displacement of nucleus, apophyseal bone cartilage and annular tissue.
Back pain can be classified into stages of acute, chronic and recurrent.
Back pain is caused by :
- Changes of the intervertebral disc
- Muscular injury
- Incorrect posture
- Spine fracture(rare)
Example : sneezing, coughing, lifting weight , Squatting
Symptoms of Slipped disc :
- back pain
- sciatica(referred pain and weakness of the limb especially the lower limb)
- Cauda equina syndrome ( unable to control bladder and bowel movement)(rare)
Objective of physiotherapy
- To reduce pain
- To strengthen back muscle and abdominal
- To maintain body range of motion
- To improve the body range of motion
- To help patient to be able to perform their daily activity independently without pain
Signs & Symptoms
- Acute back pain
Pain experienced within 1 to 3 months
- Chronic back pain
Pain experienced for more than 3 months.
- Recurrent back pain
Recurrent back pain within 3months.
Complications
Limitation of daily activity due to pain.
Prevention
- Make sure correct posture during sitting, standing, lying down or during engaging in daily activities with taking in consider of these matters:
Lying down
- Choose a firm pillow. This will support the spine better.
Lying position: side lying with trunk slight flexed forward and a pillow placed in between the knees.
Walking
- Wear comfortable shoes with low heels.
Sitting
- Use chair with back rest which can support the back.
- Use a small pillow or lumbar roll to support the back.
Standing
- If standing for prolonged time, rest the legs alternately on a small stool.
- Proper lifting/carrying techniques
- Do exercise regularly
- Take care of the body weight
Increase general body fitness
Rehabilitation
1. Pain management
- Ice pack – management of acute pain
How to apply: wrap the icepack with wet towel and put it on pain site for 15 minutes.
There should be no ointment applied on the pain site before putting the icepack
- hot pack – management of chronic and recurrent pain
How to apply: wrap the hot pack with enough number of towel (not too hot) and put it on pain site for 20 minutes. There should be no ointment applied on the skin.
2. Back pain exercise Program
|
|
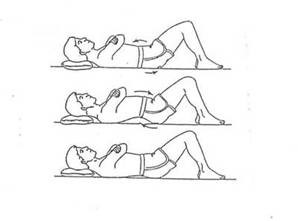
Pelvic Tilt Position : lie down on a flat surface |
|
|
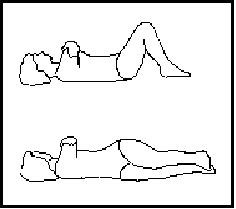
Hip Rolling Position: lie down on flat surface, with both knee bent.
|
|
|
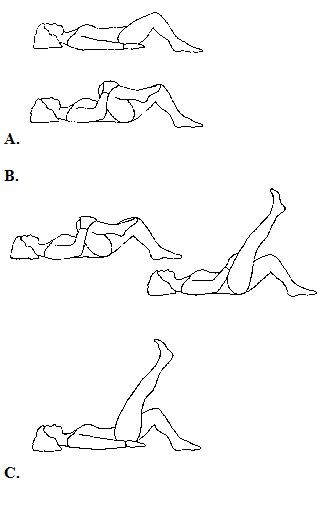
Lower Abdominal Exercise Position: lie down on flat surface, with both knee bent 1) Bring the right knee to the chest and hold for 5 seconds. Repeat on the left leg. 2) Lift the right leg up with knee straight position. Later lower it down slowly. Repeat it on the left leg. Repeat for minimum 5 times |
|
|
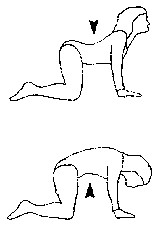
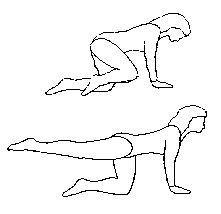
Cat and camel Position : kneeling
|
|
|
Hip Extension Position: Kneeling |
3. Lumbar Stabilization Exercises
- Position: lie down on flat surface with both knees bent.
- Straighten the right knee, contract the abdominal muscle and maintain the body in neutral alignment. Then lift the right leg 12 inches from the floor and hold for 3 seconds. Then slowly lower the right leg to the floor. Do it again on the left leg.
- Repeat for 5 times.
References
1. Baker, ADL. And Burke (2008) Back pain: Background, aetiology, diagnosis and treatment; The Foundation years 4(8), 302-308.
2. Boucher, P. and Robidoux, S. (2014) Lumbar disc herniation and cauda equine syndrome following spinal manipulative therapy: A review of six court decisions in Canada; Journal of forensic of legal medicine 22, 159-169.
3. Care protocol Low Back Pain oleh Jawatankuasa teknikal Profesion Fisioterapi, KKM
4. Janie Hampton, 1992, Aches and Pain, Oxford Health Publications for the international League Against Rheumatism.
5. Marilyn Moffat, 2006, Muskuloskleletal Essentials, Applying the preferred Physical Therapist Practice Patterns, SLACK Incorporated
6. Tarek, M. Khalil, 1993, Ergonomics in Back Pain, A Guide to Prevention and Rehabilitation,New York, Van Nostrand Reinhold
7. www. Patient.co.uk/health/ prolapsed-Disc-(Slipped dics).htm.
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer | : | Sia Lee Lee |
| Translator | : | Saravanan a/l Rajadurai |
| Accreditor | : | Daaljit Singh a/l Harbachan Singh |
| Reviewer | : | Halimah bt. Hashim |