Introduction
Smoking is bad for you . Please do not start if you are not smoking right now. Evidence have shown it is harmful to your body and people around you.
Malaysians smoked 23.7 billion cigarettes per year and from 18 billion sticks in 1998. (1) The number of smokers rose from 3.1 million in 2007 to 4.7 million in 2011 (2)
Smoking-related disease is the number one killer in this country, which resulted in about 10,000 death.
49 percent of adult males smoked in Malaysia, well above smoking in developed countries such as the UK (38 percent), the United States (35 percent) and Sweden (30 percent).
Large number of smokers started smoking in their teens, with the average age at 19 years old. In 1985, 9.8 percent of adolescent smoke and increased to 18 percent in 2000. A disturbing phenomenon is that more and more girls begin smoking, particularly in the city. It has increased from one to eight per cent. It is estimated that every day, 50 teenagers start smoking.
Studies have shown that each cigarette has about 4,000 poisonous substances that are inhaled into the body when a person smokes, which includes tar, nicotine and carbon monoxide.(1)
Why is it important to avoid or stop smoking?
- Smoking is harmful to you or people around you (secondhand or environmental tobacco smoke (ETS).
- Studies have shown,
- Smokers have a three-fold increased in getting oral cancer.
- Possibility of getting oral cancer is dosage and length related. The more you smoke and the longer you smoke will increase that possibility.
- By stop smoking, you will decrease the possibility of getting oral cancer. Stop smoking within 1 – 4 years, reduction is around 35%, while more than 20 years of stop smoking, the possibility is the same as non-smoker of getting oral cancer.
- Smoking is a risk factor for gum disease. Many smokers have severe gum disease and usually detected late. Stopping the smoking habits will improve your gum health upon treatment.
What are the bad effects of smoking?
Smoking can cause many oral health problems including :
- Staining of the teeth.
- Bad breath (halitosis).
- Gum (periodontal) disease.
- Oral cancer.
It is also associated with many other medical conditions e.g.
- Lung cancer.
- High blood pressure.
- Stroke.
- Heart disease.
- Impotence.
What can you do if you are a smoker?
You have to stop smoking. If you want to stop, make sure you :
- Do mouth self-examination.
- Have regular visits to your dentist.
Are there any special tips to kick the habit?
It is not easy to stop smoking. You need a strong will and spiritual power, plus good support from your family and friends.
Some tips to quit smoking :
- Set a date to quit and make reminder notes.
- Write down the reasons you want to quit.
- Be confident, always think positively and tell yourself “I am not a smoker”.
- Get support , you need it, from friends and family members around you. (Your doctor or dentist is also a good source of help and support. See list of Quit Smoking Clinics).
- Overcome the urge to smoke :
- chew sugarless chewing gum
- exercise more
- take bath frequently
- Use nicotine replacement therapy with advice from the physician.
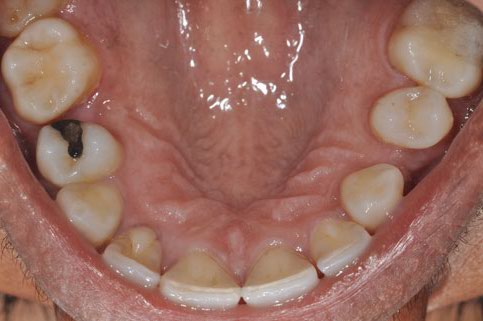
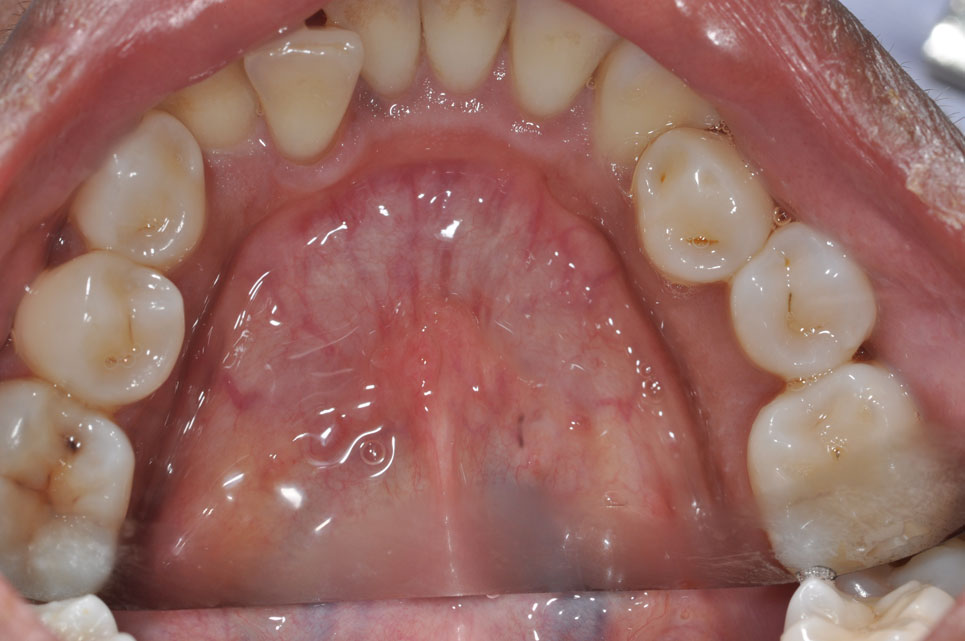
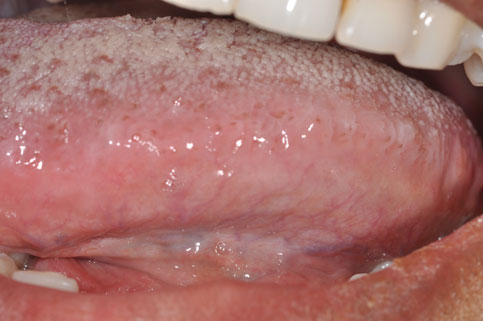
Mouth Self Examination
- Stand in front of a mirror under good lighting, look at these places:
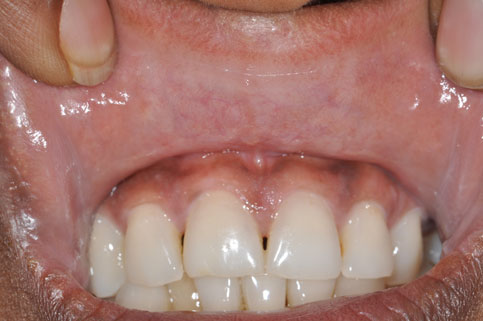
- Lips, upper and lower, inside and outside the mouth
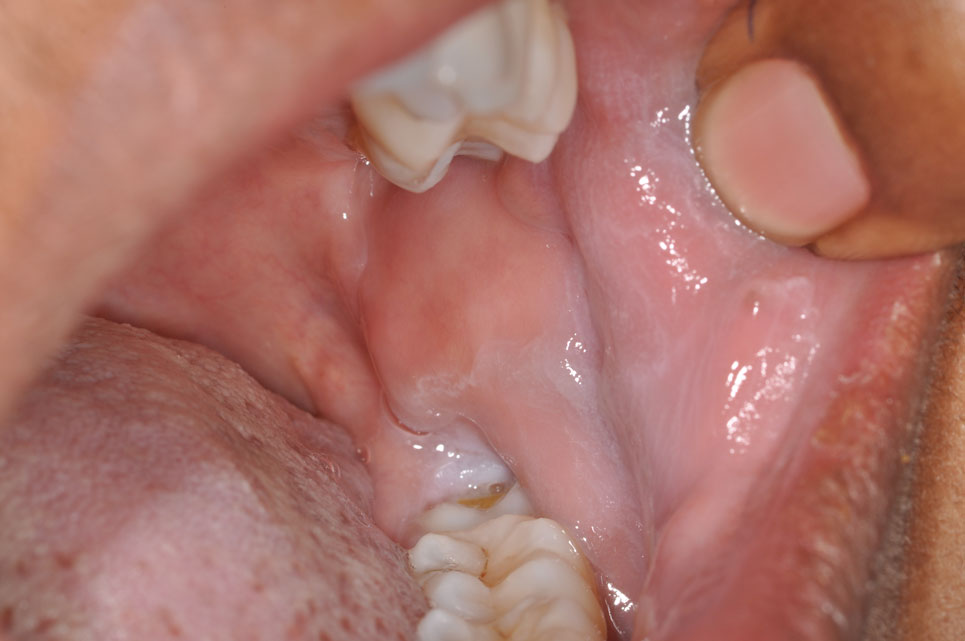
- Inside the cheek, left and right.
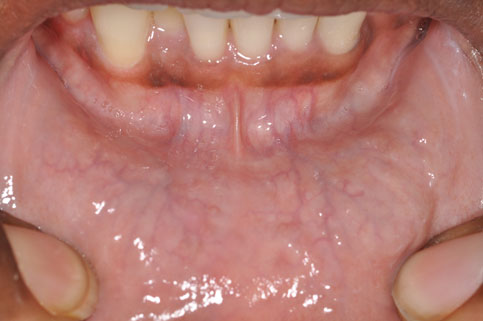
- Tongue and floor of the mouth
- Palate
- Gum
- Look for white or red patches
- Look for ulcers . Ulcer that does not heal after 2 weeks is of particular importance.
- Use your thumbs to check below the mandible for any pain, lumps or changes in the texture of the tissues.
- If you notice any of those mentioned above, or you are not sure, consult your dentist.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
References
- http://www.ikim.gov.my/index.php/ms/berita-harian/6809-setiap-hari-50-remaja-mulakan-tabiat-merokok
- http://www.kosmo.com.my/
| Last Review | : | 25 June 2014 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Azillah bt. Mohd Ali |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Che Noor Aini bt. Che Omar |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Rapeah bt. Mohd Yassin |
| Dr. Ahmad Sharifuddin b. Mohd Asari |







