What Is Strabismus And What Is Squint?
Strabismus is also known as squint. It occurs when the two eyes are not aligned and point in different directions. One eye is looking straight while the other points inwards, outwards, upwards or downwards. It may run in families. It occurs in 2 – 5% of all children.
What Causes Strabismus?
- Most cases of strabismus are of unknown cause.
- It may be caused by unequal pulling of muscles of one side of the eye or paralysis of the eye muscles.
- Far sightedness (hyperopia) may cause the eyes to turn inwards.
- Strabismus is especially common among children with disorders of the brain such as Cerebral Palsy, Down Syndrome, hydrocephalus and brain tumours.
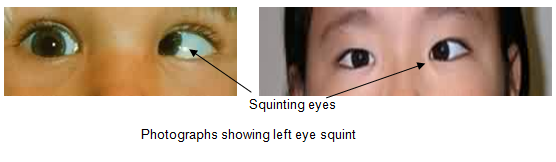
Examples of squint :
 |
|---|
What Are The Signs Or Symptoms Of Strabismus?
- The main symptom and sign of strabismus is misaligned eyes.
- Strabismus may be persistent or may come and go (intermittent).
- Newborns often have strabismus due to undeveloped vision, but this disappears as the infant grows.
- True strabismus does not disappear with growth.
What Are The Effects Of Strabismus?
- Strabismus may cause reduced vision in the affected eye due to amblyopia (lazy eye). If it is not treated early enough (before the child is 10 years old), vision of the affected eye will be permanently reduced. The earlier the treatment for amblypia instituted, the better will be the prognosis.
- Binocular vision or 3 dimensional vision is used to judge depth. This may be impaired in children with strabismus.
How Can It Be Treated?
- Strabismus/squint always require early assessment by an eye doctor.
- Eye glasses may be required to correct refractive errors like far-sightedness (hyperopia).
- In children who develop amblyopia in the eye due to squint, patching the ‘good eye’ may help to improve the vision in the squinting eye. This may not be successful if treatment is delayed. Treatment needs to be started in the first few years of life while the visual system is developing.
- Surgery can correct squints and is usually an effective treatment for squint. However, it is not a substitute for glasses or amblyopia therapy. During the surgery, certain muscles are repositioned. After surgery, children are usually able to resume normal activities within a few days.
- Injection of the eye muscles with Botox injection may be helpful in correcting the squint in some cases, but it is only a temporary measure.
| Last reviewed | : | 10 May 2012 |
| Content Writer | : | Dr. R. Sukumar A/L Rajaretnam |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Salmah Binti Othman |







