What is Snoring?
Snoring is an audible breathing noise produced when a person has a partially blocked upper respiratory tract. You snore when something blocks the free flow of air through the passages at the back of your mouth and nose.
The sound is caused by tissues at the top of the airway that strike each other and vibrate. Snoring increases with age and is usually harmless.
Causes of snoring
- Poor muscle tone in the tongue, soft palate and throat. When muscles are too relaxed, either from alcohol or drugs that cause reduced muscle tone, the tongue falls backwards into the airway or the throat muscles draw in from the sides of the throat into the airway. This can also happen during deep sleep.
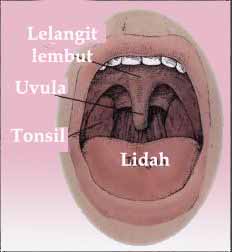
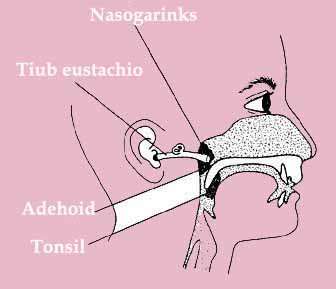
- Excessive bulkiness of throat tissue. Children with large tonsils and adenoids often snore. Overweight people have bulky neck tissue too.
- Long soft palate and/or uvula. A long uvula narrows the opening from the nose into the throat. Excessive vibrations from this tissue can cause snoring.
- Obstructed nasal airways. A stuffy or blocked nose requires extra effort to pull air through it. This creates an exaggerated vacuum in the throat, and pulls the floppy tissues of the throat, and snoring results. Among the causes are deviated nose (nasal septum), nasal polyps and sinusitis.
 |
 |
Complications
Snoring can also be a sign of a serious sleep disorder called sleep apnea. This means you stop breathing for periods of more than 10 seconds at a time while you sleep. Sleep apnea is a potentially dangerous medical condition, but there is treatment that can help.
Treatment
Can heavy snoring be cured?
Heavy snorers, those who snore in any position that are disruptive to the family, should seek medical advice to ensure that sleep apnea is not a problem.
An ear, nose and throat specialist (otorhinolaryngologist) will provide a thorough examination of the nose, mouth, throat, palate, and neck.
A sleep study in a laboratory environment may be necessary to determine how serious the snoring is and what effects it has on the snorer’s health.
Treatment for snoring
Treatment depends on the diagnosis. An examination will reveal if the snoring is caused by nasal allergy, infection, deformity or tonsils and adenoids. Accordingly the treatment can be given.
Prevention
Tips for reducing snoring:
- Lose weight if you are overweight
- Cut down or eliminate alcohol and other sedatives at bedtime
- Avoid tranquilizers, sleeping pills, and antihistamines before bedtime
- Avoid alcohol for at least four hours and heavy meals or snacks for three hours before retiring
- Adopt a healthy and athletic lifestyle to develop good muscle tone. This also helps to lose weight
- Establish a regular sleeping pattern
- Sleep on your side rather than on your back
- Tilt the head of your bed upwards by about four inches
| Last Reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Nazrila Hairizan bt. Nasir |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Wan Fadhilah bte Wan Ismail |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Nazhatussima bt. Suhaili |







