What is road traffic crash?
Malaysia is recorded as among the top countries that shows highest in accident and death rate in the world. Statistics issued by the Malaysian Institute of Road Safety Research (MIROS) between year 2000 to 2014 showed a significant increase in the number of road traffic crashs, from 250,429 cases to 476,196 cases. Total death resulting from road traffic crash on the other hand is more than 6000 cases each year.
Studies done on February 2014 by the Transport Research Institute, University of Michigan, USA has ranked Malaysia as the top 17 in road fatalities rate in the world. This study had used year 2008 World Health Organisation (WHO) data which also involves 193 other countries.
According to the Road Transport Act 1987, road traffic crash is defined as accidents or occurrence whereby damage or injury is caused to any person, property, vehicle, structure or animal and occurs in any public road including bridge, tunnels, lay-bye, interchanges, overpasses, toll plazas and so on.
Road traffic crash involves either motor vehicles, bicycles, tricycles, pedestrians and other types of vehicles.
According to the World Health Organization’s (WHO’s), road traffic crash is defined as “collision or incident that may or may not lead to injury, occur on a public road and involving at least one moving vehicle”.
Types of Road Traffic Crash
-
Pedestrian
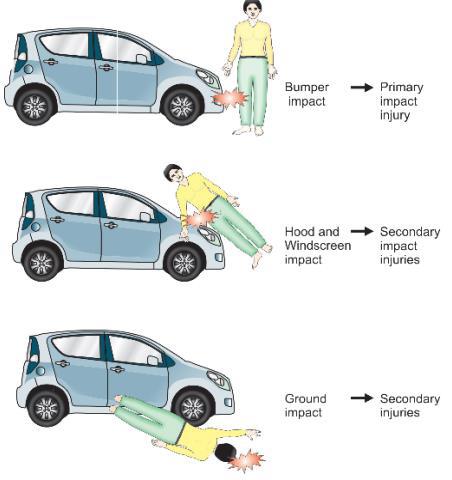
Generally injuries sustained by pedestrian can be divided into three types. Primary injury occurs during the initial collision direct to pedestrian. As a matter of fact, due to the first impact of the collision, victim usually will be thrown into direct contact with the vehicle. This is known as secondary injury. Tertiary injury on the other hand resulted due to victim thrown onto the ground.
The nature of pedestrian injuries depends on the speed and which part of the vehicle that collide them. In hit-and-run case, investigators will try to identify the offender vehicle by finding a match between injury mark and the location of collision impact on the vehicle. For example, a collision between a pedestrian victim with front car bumper tends to produce primary injury on victim’s leg roughly at the same height as the bumper of the car.
The vehicle speed during collision also affects the nature of the accident. Low-speed collision (the vehicle moving around 20 km/h) would usually result pedestrian to end up in front or to the side of the vehicle. In medium-speed (20-60 km/h), the victim will usually will be tossed over the vehicle front bonnet or windscreen, and will be thrown into the air and then fall off to the ground in a high-speed collision (60-100km/h). A low-speed collision often results in the pedestrian victim being run over by the involved vehicle, whereas in the case of high-speed can cause severe head trauma when the pedestrian hits the ground surface. -
Driver Passenger
Collision between a vehicle with another vehicle or with a structure at the roadside could injure the driver and passenger.
Injuries can occur when the driver and passengers hit the hard component inside the vehicle during collision. In addition, injuries may occur if victim is thrown out from the vehicle.
Driver can suffer serious injuries when his chest hits the steering wheel. However, seat belt worn by driver can prevent him from hitting onto the steering wheel or smashed into the windshield and then thrown out of the car, which can cause massive trauma.
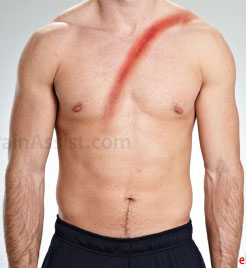
Determining whether the occupant uses seat belt or not during an accident is an important part in any road traffic investigation. In addition, investigation to determine the identity of the driver and passenger also necessary to determine the liability in that accident. Linear abrasions caused by the compression of seat belt could help to identify the seating position of the victim in the vehicle and thus can determine the actual driver during the accident
- Two-wheeled vehicle rider
In developing countries, road use is dominated by two-wheeled vehicles such as motorcycles. Motorcyclist have the highest risk of traffic collision case especially for head injury.
In Malaysia, fatal accident case is very significant among motorcyclist looking at national statistics issued by MIROS. Road fatalities statistics from year 2000 to 2014 showed that motorcyclist contributed the highest mortality which is about 50% of the total deaths.
In contrast to developed countries, accidents involving motorcycles are relatively low. In those countries, motorcycle riding is considered a leisure activity whereas developing countries use bike as basic and important transportation.
Role of forensic in Road Traffic Crash
- Accident reconstruction
One of the forensic role in road traffic crash investigation is accident reconstruction. Accident reconstruction is carried out to determine how the crash occurred based on the available physical evidence. The element of interest in road traffic crash investigation are vehicle speed, direction of travel and vehicle position on the roadway when the collision occurred.
Classical reconstruction process usually begins with post-crash data and working to determine the sequence of events that occurred before the accident. The process of analyzing and using physical evidence to understand how the accident happen is like arranging the pieces of puzzle (jigsaw puzzle). The pieces of puzzle that are complete will be able to determine the original image. In the end, the quantity and quality of physical evidence would determine what can be learned about the accident.
Physical evidences that are commonly found are tire marks, damage of the vehicle, debris pattern and vehicle end position after collision. Tire marks left on the road before, during and after the collision can provide important information regarding the accident.
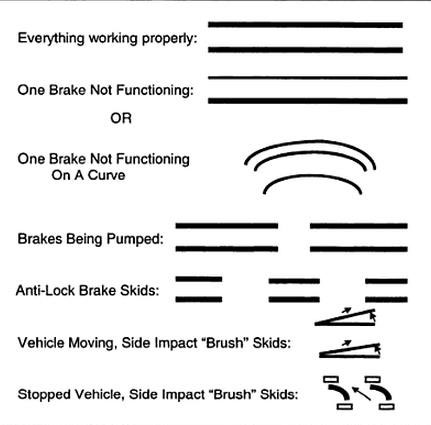
The position and orientation of tire marks indicate the route of the vehicle before and after the crash. The changes in direction of tire marks, gouges and scrapes on the road surface can point out the vehicle position during impact. Whereas the nature and dimension of tire marks enable investigator to calculate the speed of one or more vehicles which is a vital component of analysis of cause of the accident.
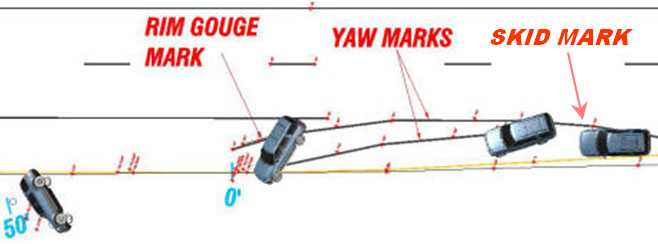
Tire mark that is often found is skid mark. It occurs when the vehicle wheel stops rolling after brake and caused the tire to slide or drag along the surface of the road. Vehicle speed during collision can be calculated based on the length of the skid mark by using certain formula. In addition, skid mark can tell about the brake on vehicle that laid down the skids. Tire mark also can be seen when the driver change the wheel direction dramatically, in order to avoid collision or when taking a sharp cornering with high speed. Tire deviation effect from the original route is known as yaw mark. Yaw mark is usually curved and has long line pattern across it.
Other mark that can be found is gouge mark on the road. Gouge mark is caused by the wheel rims when a tire either goes flat or comes off the wheel. Besides, it can also occur when the wheel is turned sharply at high rate of speed. This gouge mark help to determine whether a flat tire causes the accident or the tire went flat as a result of the accident
Skid Marks
Source:http://aug-cdn.comYaw Mark
Source: http://www.caranddriver.comGouge Mark
Source:https://underthehollywoodsign.wordpress.comDamage undergone by vehicle on the other hand can give qualitative and quantitative information. The nature and position of the vehicle damaged will determine the direction from which the impact force of collision and vehicle position during a collision. The extent of vehicle damage may help investigators to estimate the vehicle speed during the collision. Among the important reason why the speed of the vehicle should be determined in the accident investigation is because the speed factor is often the cause of any accident. For example, a driver can be skidded and lost control when turn at the corner with high speed and cause an accident.
The relative position the car and vehicle that collide it can be determined by looking the front damage
Source: http://www.marshu.comAccident reconstruction process
Source: http://www.evansar.com - Determine whether accidental, suicidal or homicidal
Investigation of road traffic crash conducted by the authorities also includes the classification of the manner of death, i.e. accidental, suicide or homicidal. All information derived from the investigation at the scene of accident, interviews conducted on witnesses and forensic medicolegal autopsy examination on victim will be used to determine the manner of death in road traffic crash cases.
During the autopsy, medical officer in charge will examine injuries sustained by the victim. Other aspects that will be examined are the types of injuries and differences between injuries made by victim itself, injured by others or injuries sustained from the accident. The injuries found will determined other contribution factors. Apart from that, specimens like blood and urine from the victim will be taken and sent to laboratory for drugs testing and alcohol depending on the need of the investigation. The autopsy findings will determine the cause of death and manner of death of the victim that will assist in the police investigation.
Conclusion
The utilisation of knowledge in forensic field is essential in road traffic crash investigation. During investigation process, various evidence and information will be used to support one another. Apart from determining the cause of the accident, the findings of accident investigation will eventually be used by the authorities to educate the public and to improve on the road safety system in the country.
References
-
Akta 333, Akta Pengangkutan Jalann Raya 1987 seksyen 2 (Malaysia). Diambil dari Portal Jabatan Pengangkutan Jalan Malaysia: http://www.jpj.gov.my/web/eng/act-333.
-
Dina Murad (2014). Malaysia Has 17th Most Dangerous Roads in the World, According to Michigan University Research. Diambil pada 30 Jun, 2015, dari http://www.thestar.com.my/News/Nation/2014/ 02/22/Nations-with-deadliest-roads-Malaysia-17th/.
-
Jamieson, A. & Moenssens, A. (2009). Reconstruction: Accident. Wiley Encyclopedia of Forensic Science, vol. 5, 2250-2256.
-
Kibayashi, K., Shimada, R. & Nakao K. (2014). Fatal Traffic Accidents and Forensic Medicine. International Association of Traffic and Safety Sciences,38, 71-76.
-
Liu BC et al. (2004). Helmets for Preventing Injury in Motorcycle Riders. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (2):CD004333.
-
Malaysia Institute of Road Safety Research (2015). Statistics and Accident Characteristics Involving Motorcycles in Malaysia. Diambil pada 30 Jun, 2015, dari http://www.miros.gov.my/c/document_ library/get_file?uuid=9d24d742-5abd-481d-abf5-9128c1384128&groupId=26426
-
Malaysia Institute of Road Safety Research (2015). General Road Accident Data in Malaysia (1997 – 2014). Diambil pada 30 Jun, 2015, dari http://www.miros.gov.my/web/guest/road
-
Mohamad Ghazali, M., Khairil Anuar, M.I. & Mohd Pozi, M.T. (2011). Children, Youth and Road Environment: Road Traffic Accident. Asian Journal Of Environment-Behaviour Studies, Vol 2, No. 6.
-
Ooi, S. S., Wong, S. V., Radin Umar, R. S., Azhar, A. A. & Megat Ahmad, M. M. H. (2005). Cervical Spine Injuries Sustained by Motorcyclists in Road Crashes in Malaysia. International Journal of Crash, 10(2).
-
Peden, M, Oyegbite K, Ozanne-Smith J, et al.. (2008). World Report on Child Injury Prevention. Geneva: World Health Organization. Diambil pada 30 Jun, 2015, dari http://whqlibdoc.who. int/publications/2008/9789241563574_eng.pdf?ua=1.
-
Rudram, D. (2000). Accident Investigation/ Determination of The Cause: Overview. Encyclopedia of Forensic Science, Three-Volume Set, 9-16.
-
Ritter, F. D. (2000) Successful Personal Injury Investigation: Master the Techniques of Finding the Facts that Win Cases for Plaintiff Attorneys. Boleh didapati dari https://books.google.com.my/books /about/Successful_Personal_Injury_Investigation.html?id=2eS5V6PADrUC&redir_esc=y.
-
Singh, N. (2014). Road Traffic Injury [Power Point slides]. Diambil pada 30 Jun, 2015 dari: http://www.slideshare.net/ neharikasingh9678/road-traffic-injury.
-
Worley, H. (2006). Road Traffic Accidents Increase Dramatically Worldwide. Diambil pada 30 Jun, 2015, dari Population Reference Bureau PRB: http://www.prb.org/Articles/2006/RoadTrafficAccidents IncreaseDramaticallyWorldwide.aspx.
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer | : | Asrul Fahmi bin Abdul Mutalib |
| Accreditor / Reviewer | : | Dr. Khoo Lay See |