Introduction
Tooth brushing should be performed daily for personal hygiene and grooming.
Daily tooth brushing with fluoridated toothpaste prevents dental caries. Worldwide decline in dental caries has been attributed to the use of fluorides especially that in fluoridated toothpaste.
Proper Usage Of Fluoridated Toothpaste
Brushing with children’s fluoride toothpaste can help ensure that your child’s teeth receive the benefits of fluoride in strengthening enamel and preventing cavities
Use of fluoridated toothpaste can effect a reduction in caries in children’s permanent and primary teeth.
The Do’s and Don’ts of Fluoride Toothpaste Usage for Children
Do
- Use only a smear of children’s toothpaste for young children ( the under-2 ) ( Children’s toothpaste contains 600ppm or less fluoride )
- Brush twice daily
- Brush last thing at night
Don’t
- Do not recommend a toothpaste containing more than 600ppm fluoride for children under six years unless assessed as high caries,
- Do not rinse after brushing ( just spit )
For young patients determined as “high risk”, by dentists, even the under sixes should use a toothpaste containing higher fluoride levels ( up to 1,000 ppm ) or adult’s toothpaste.
Quantity of fluoride toothpaste recommended ;
For children 6 years below
Use a small quantity of children’s fluoridated toothpaste i.e. 0.25 to 0.5g or the equivalent of a groundnut-size or strip less than 5mm long* as in Fig.1
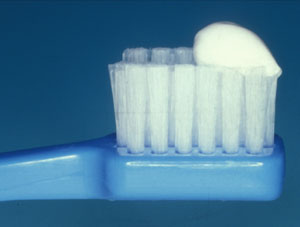
Figure 1 : Approximation of toothpaste’s quantity, groundnut size.
For children 2 years below, use just a smear layer of children.s toothpaste.
- Dispensing of toothpaste on the toothbrush should be controlled by parents
- Teach your child to spit out the toothpaste, not swallow it, after brushing
Effects Of Excessive Fluoride Intake
Excessive fluoride intake may occur in children is through ingestion of fluoridated toothpaste.
Some children simply like the taste of flavoured fluoridated toothpaste and swallow it instead of spitting it out.
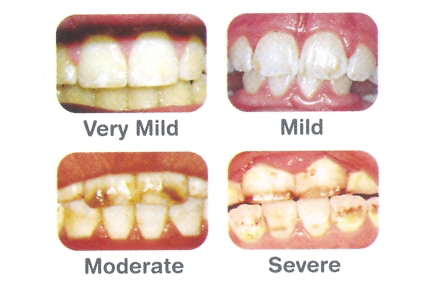
Excessive fluoride intake at a young age can lead to the development of fluoride-induced tooth defects (fluorosis).
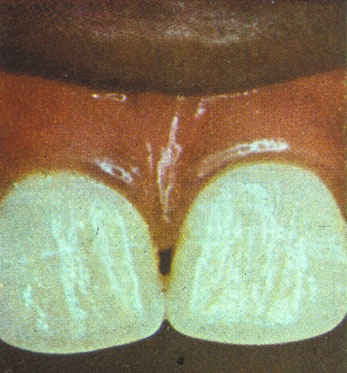
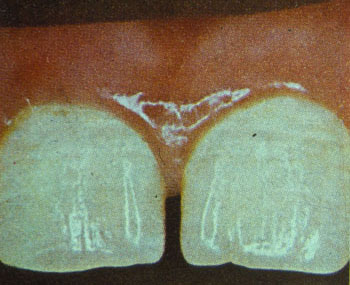
Severity may vary from white speckled enamel to pitted brown enamel. The discolouration is more marked in the permanent front teeth. As the front teeth are important in enhancing your child’s smile the tooth defects can result in low self esteem and confidence.
 |
 |
|
| Normal teeth | Teeth with mild fluorosis | |
 |
||
| Figure 2 : Severity Of Fluorosis | ||
Treatment Of Enamel Effects
Enamel fluorosis can be treated. The appearance of teeth affected by fluorosis can be greatly improved by a variety of treatment in esthetic dentistry. If your child suffers from severe enamel fluorosis, your pediatric dentist can tell you about dental procedures that can enhance your child’s smile and self-confidence.
| Last reviewed | : | 20 April 2012 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Laila bt. Abdul Jalil |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Ganasalingam a/l Sockalingam |







